Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (28)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
Ensuring Optimal Performance: Best Practices For Bearing Mounting Procedures
Introduction
Bearing Mounting is essential to ensure the proper operation of mechanical equipment. By properly mounting bearing, they can effectively support and guide the rotational or linear motion of a shaft.
In addition, bearing mounting also reduces friction, transfers loads, dampens vibration and absorbs shocks as well as adjusts clearance and alignment, improving the operational efficiency, life and reliability of the equipment.
Therefore, proper bearing mounting not only reduces maintenance costs and downtime, but also improves productivity and product quality.
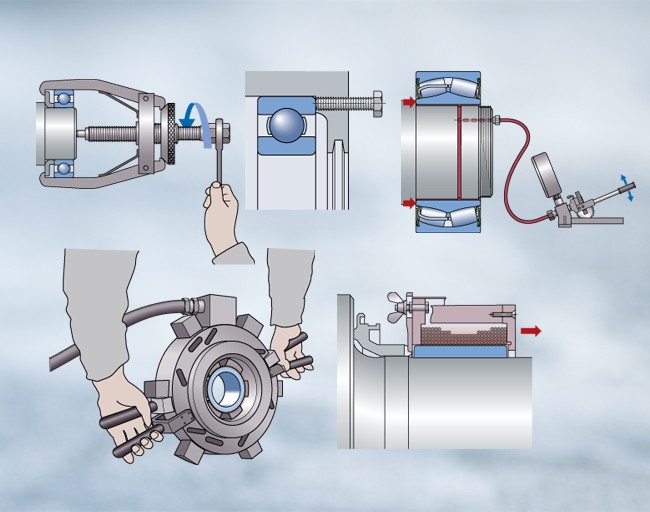
There are a number of different methods for Bearing Mounting. The best method for a particular application will depend on the type of bearing, the size of the bearing, the material of the bearing, and the environment in which the bearing will be operating. Some of the most common methods for Bearing Mounting include:
- Press fit
- Press and Taper Fit
- Keyed fit
- Heat mounting
- Mechanical mounting
- Shrink fit
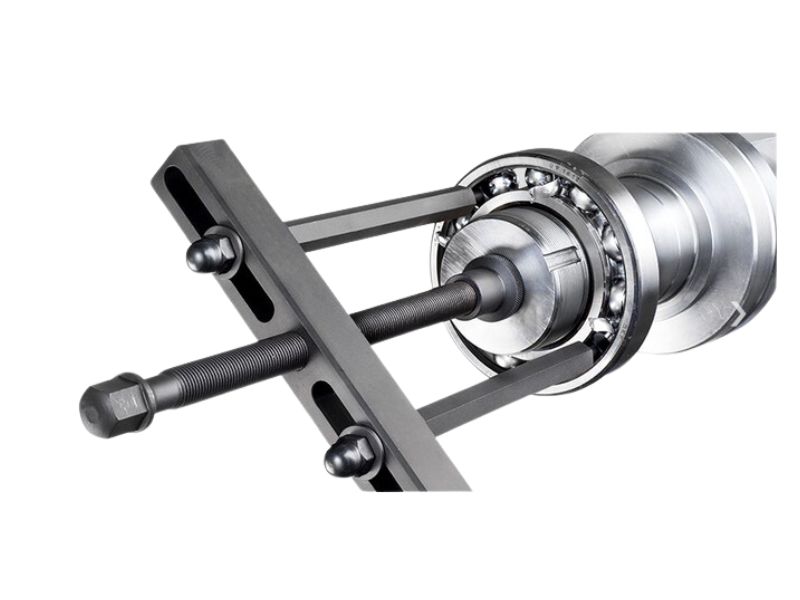


Press Fit
A press fit is a type of interference fit in which the bearing is pressed into a housing that is slightly smaller than the bearing. The interference between the bearing and the housing creates a tight fit that prevents the bearing from rotating.
Press fits are typically used for small bearings that are made from hard materials, such as steel.
Press and Taper Fit
A press and taper fit is a type of interference fit in which the bearing is pressed into a housing that has a taper. The taper creates a tight fit that prevents the bearing from rotating.
Press and taper fits are typically used for bearings that will be subjected to high loads.
Keyed Fit
A keyed fit is a type of interference fit in which a key is inserted into a keyway in the bearing and the housing. The key prevents the bearing from rotating.
Keyed fits are typically used for bearings that will be subjected to high loads.
Heat mounting
Heat mounting works by heating the bearing or shaft or housing, causing it to expand and then mounting the bearing in place. After the bearing cools and shrinks, a tight fit will be formed, improving the stability and reliability of the installation. Especially suitable for large bearings or situations that require large installation force.
Mechanical mounting
Mechanical mounting is the installation of a bearing onto a shaft or housing using manual operations or simple tools. This method is relatively simple, low-cost, and can be applied in a variety of situations.
Shrink fit
Shrink fit uses the principle of low temperature to shrink the size of the bearing or shaft or bearing seat by cooling it, and then install the bearing in place. Shrink fit is suitable for situations where a high degree of tightness is required, such as high-speed rotation or high load.
Preparation For Bearing Mounting
Before bearing mounting, First, confirm the bearing type and size, and understand the mounting requirements according to the bearing specifications;
Prepare and check whether the necessary tools and equipment are suitable and in good condition, and ensure that the bearings, shafts, seats and mounting environment are clean.
Also, choose and apply lubricant correctly to avoid excess or deficiency. Before mounting, conduct a comprehensive inspection to confirm that all parts and tools are ready.
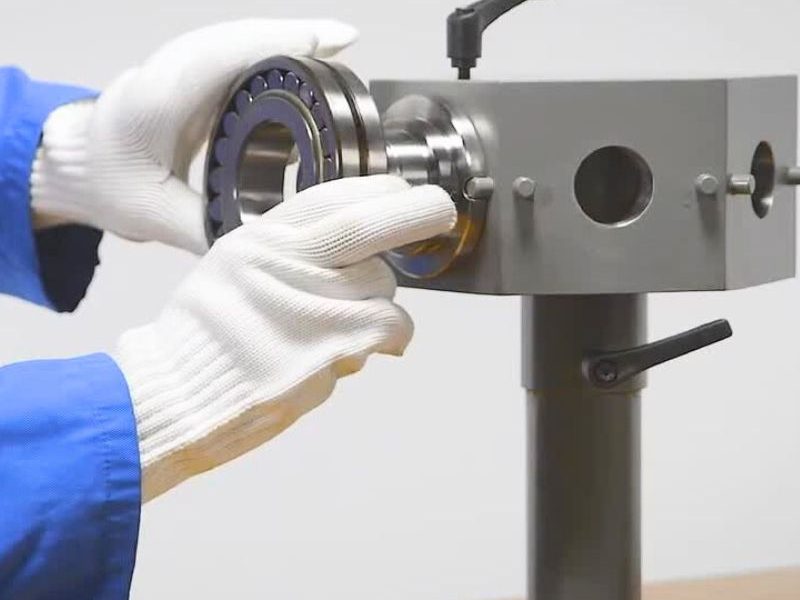
Bearing Mounting Steps
- Clean the mounting location to ensure there is no contamination and foreign matter.
- Check bearings and fittings for damage.
- Choose the appropriate mounting method according to the bearing type and size.
- Prepare necessary tools and equipment, such as heaters, press tools, etc.
- Appropriate heating or cooling preconditioning of bearings and/or journals.
- Be careful when mounting bearings to avoid shock and distortion.
- Complete bearing fixing and adjustment according to specification requirements.
- Inspect after mounting to confirm the bearing status and assembly quality.
- Apply an appropriate amount of lubricant to help the bearing operate normally.
- Record relevant installation data to prepare for maintenance.
But be aware that bearings cannot be cleaned (unless otherwise stated in the instructions). They are protected from oxidation by a light oil film, compatible with all lubricants.
Mounting method: Mount the bearing to the shaft or bearing seat through axial pressure. It can be pushed in directly by hand, or pressed using appropriate tools and equipment (such as a press machine).
Since the fit between the inner ring of the cylindrical bore bearing and the shaft is usually a transition fit or a slight interference fit, axial positioning is relatively easy.
The mounting of cylindrical bore bearings does not require adjustment of the axial position of the inner ring, because the positioning of the bearing mainly relies on components such as shaft shoulders or stop rings.
Mounting method: Mounting of tapered bore bearings requires the use of fastening nuts, sleeves or heating methods to expand the inner ring of the bearing to achieve the required amount of interference and promote the bearing to obtain a tighter fit on the shaft.
Tapered bore bearings adjust the preload or axial clearance by changing the position of the bearing on the shaft.
Compared with cylindrical bore bearings, the mounting of tapered bore bearings is usually more complex and requires more precise operation and adjustment.
After mounting the bearing, a running test is required. Manually rotate the bearing to test whether it runs smoothly, and pay attention to whether there are abnormal sounds, vibrations or unstable friction, which may indicate mounting problems, internal damage or insufficient lubrication. Any abnormal conditions require necessary inspection or adjustment.
Check fasteners such as lock nuts and retaining rings to ensure the bearing remains stable on the shaft.
Subsequently, clean the work area to keep it tidy and orderly, and record the installation date and model number. Ensure that the bearings remain in optimal condition during operation.
Precautions
When mounting bearings, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- In most cases, it is necessary to apply an appropriate amount of grease to the inner and outer rings of the bearing before mounting to ensure initial lubrication.
- When using the hot loading method, the heating temperature should not be too high to avoid damaging the bearing, and is usually controlled below 120 degrees Celsius. Better temperature control can be achieved by using a suitable bearing heater.
- During the mounting process of bearings, they should be handled gently and slowly to avoid impact, falling or distortion. Any impact may damage the bearings.
- When mounting, it is necessary to ensure that the relative positions of the inner and outer rings of the bearing are aligned to prevent deflection or tilt.
- After mounting, check whether the assembly clearance of the bearing meets the requirements. Too tight or too loose will affect the performance.
- After the mounting is completed, appropriate locking methods (such as retaining rings, etc.) must be used to reliably fix the bearing.
Conclusion
Our comprehensive bearing mounting program covers a variety of techniques, including hot mounting, cold mounting, shrink fit and special tooling. Each method is carefully selected based on the specific bearing application, ensuring a precise, secure fit.
In addition, our strict quality control measures ensure that each bearing is mounted with extreme precision and care.
By prioritizing best practices in bearing mounting procedures, we enable our brand customers to provide quality products that meet the stringent needs of their users.
References
1.More information about ”Bearing Mounting“ from Koyo.JTEKT;
2. Some information about “Bearing Mounting” from NTN Bearing;
Detailed guide on“ bearing mounting and dismounting”