Sliding Block Bearing
Table of Contents
Definition of Sliding Block Bearing
Sliding bearings, commonly referred to as sliding blocks, are mechanical components designed to facilitate smooth and controlled motion between two surfaces in contact. Unlike rolling bearings, which involve elements like balls or rollers, sliding bearings function by allowing surfaces to slide against each other. These bearings are integral in reducing friction, minimizing wear, and ensuring efficient movement in various machinery and equipment.

FHD Bearing Company is a renowned provider of high-quality slider bearings, catering primarily to businesses in need of precision motion control solutions. FHD Bearing Company has distinguished itself as a leader in this niche, offering a comprehensive range of slider bearings with exceptional quality and performance.
Materials of Sliding Block Bearing
– Steel slider blocks are typically made from carbon steel or stainless steel. Steel slider blocks are known for their strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Stainless steel slider blocks offer corrosion resistance.
–FHD Bearing Company selects stainless steel slider bearings for harsh environments and precision applications due to their multiple benefits such as corrosion resistance, high strength, heat resistance and sanitary safety.
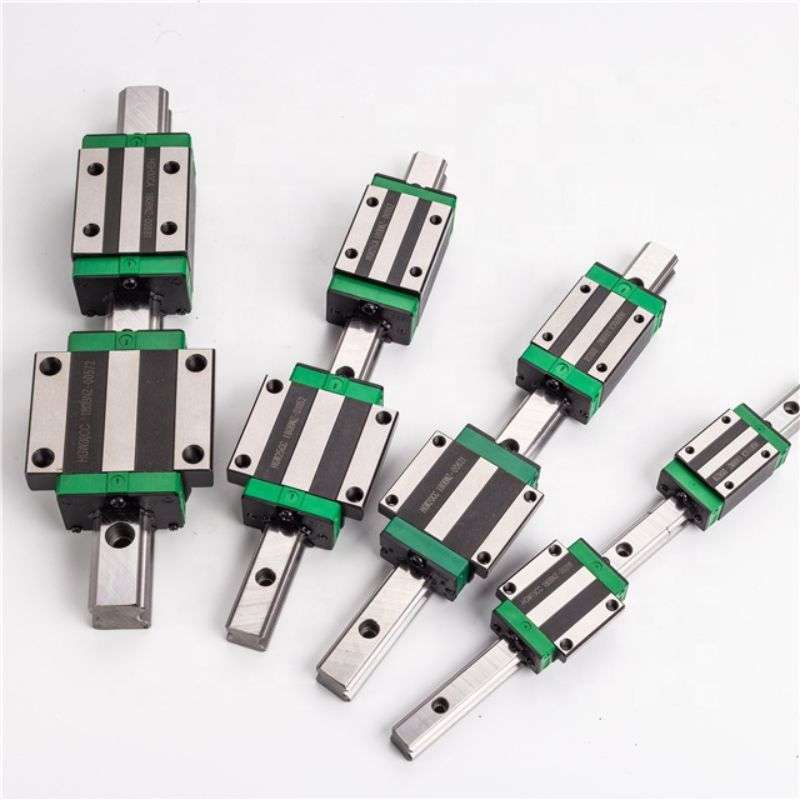

– Slider blocks made from aluminum alloys are lightweight and offer good corrosion resistance.They are suitable for applications where weight is a concern, and they provide reasonable load capacity and durability.
– FHD Bearing Company selects aluminum alloy slider bearings for a variety of applications due to their multiple advantages of light weight, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, cost-effectiveness, ease of machining and recyclability
Plastic (Polymer) Slider Blocks
– Slider blocks made from plastic materials, such as POM (Polyoxymethylene) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE).Plastic slider blocks offer low friction, are self-lubricating, and can be used in applications where resistance to moisture and chemicals is required.
Ceramic Slider Blocks
–Ceramic slider blocks are made from materials like silicon nitride or zirconia.Ceramic slider blocks provide excellent resistance to wear, high-temperature tolerance, and low friction. They are suitable for high-performance applications.
Features of Sliding Block Bearing
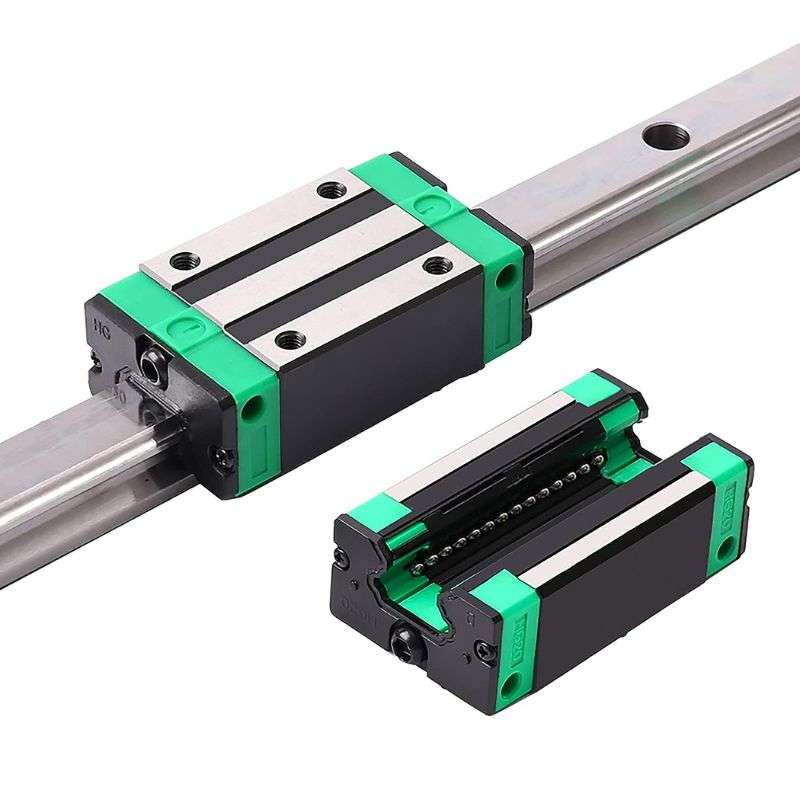

- Low Friction: Slider bearings are designed to minimize friction between moving parts, ensuring smooth and efficient motion within machinery or equipment.
- Load-Bearing Capacity: They offer excellent load-carrying capacity, making them suitable for applications with varying levels of weight and force.
- Self-Lubrication: Many slider bearings are self-lubricating, reducing the need for external lubrication and maintenance, which can result in cost savings and reduced downtime.
- Quiet Operation: Slider bearings operate with low noise levels, making them ideal for applications where noise reduction is crucial.
- Precision and Accuracy: They provide precise and accurate linear or rotational motion, ensuring consistent and reliable performance.
- Corrosion Resistance: Some slider bearings are designed to resist corrosion, making them suitable for use in harsh or corrosive environments.
- Temperature Tolerance: Slider bearings can withstand a range of temperatures, from low to high, depending on the material used, making them versatile for different applications.
- Versatility: They are used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and more, showcasing their versatility.
- Customizability: Slider bearings can be designed and manufactured to meet specific requirements, including size, shape, and material, providing flexibility for various applications.
- Ease of Installation: They are relatively easy to install and replace, reducing downtime during maintenance.
- Environmental Considerations: Some slider bearings are made from materials that are environmentally friendly and recyclable, aligning with sustainable practices.
- Longevity: When properly maintained, slider bearings can have a long service life, contributing to cost-effectiveness.
Advantages of Sliding Block Bearings
- Maintenance-Free: Many slider bearings are designed to be self-lubricating or can run without the need for frequent maintenance. This reduces downtime and lowers operational costs.
- Cost-Effective: Slider bearings are often more cost-effective than other types of bearings, such as ball bearings or roller bearings. Their simple design and manufacturing processes contribute to their affordability.
- Noise Reduction: Slider bearings operate quietly, making them ideal for applications where noise reduction is essential, such as in the automotive industry or precision machinery.
- Long Service Life: When properly maintained, slider bearings have a long service life, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated costs.
- Reduced Vibrations: Slider bearings help dampen vibrations, which is vital in applications where stability and precision are paramount.
- Simple Installation: Slider bearings are relatively easy to install and replace, which can minimize downtime during maintenance or repairs.

Taxonomy of Sliding Block Bearings
Sliding Block Bearings

Sliding Block Bearings
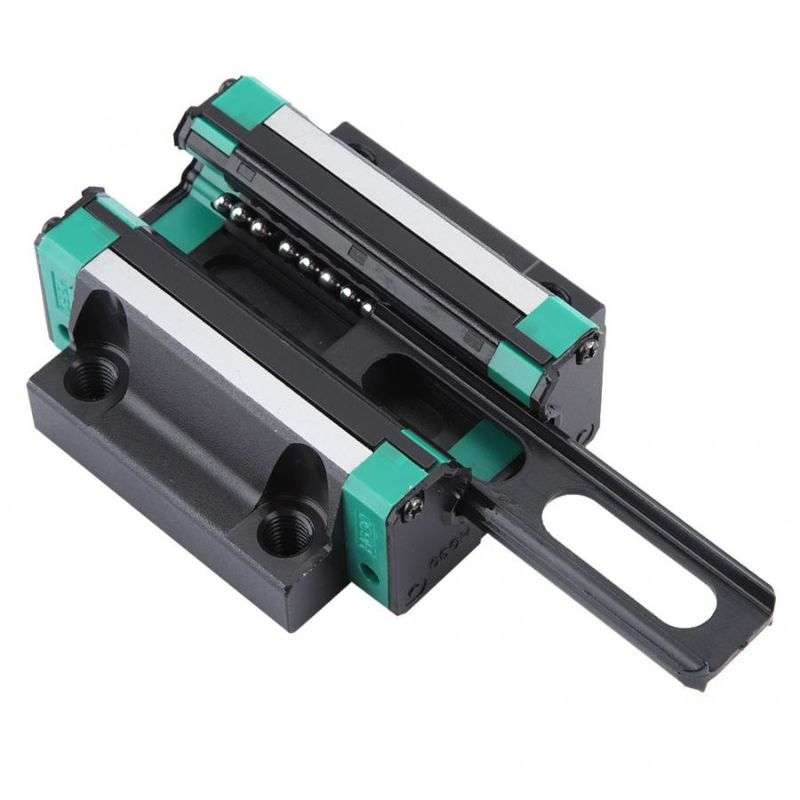
High accuracy linear guide rail slide block, which has smooth movement, low resistance and less noise, ensuring stable operation.The slide block is made of excellent bearing steel material, which has high toughness, strong wear resistance and good durability.
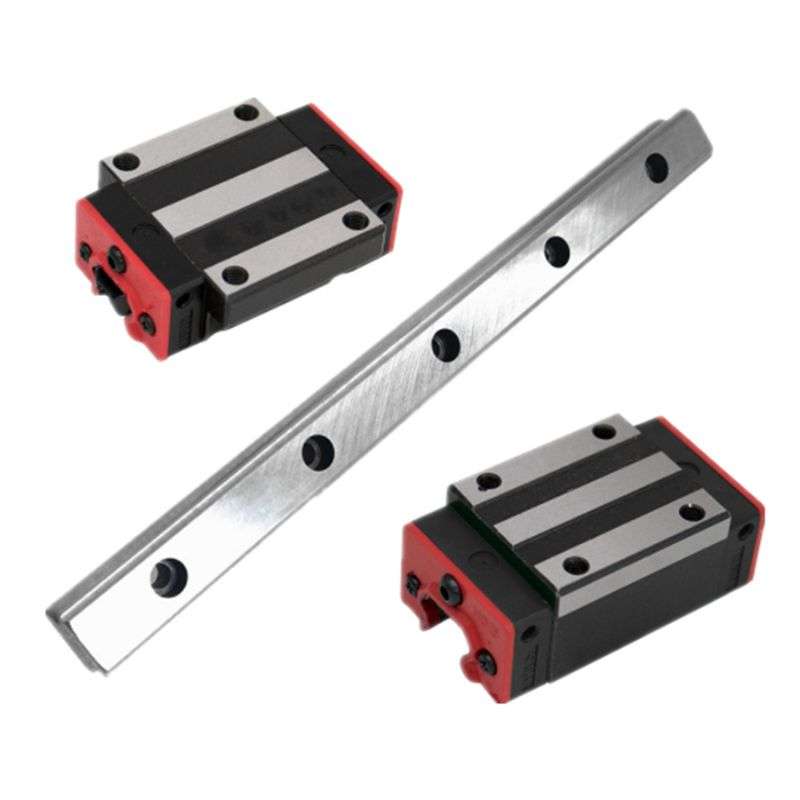

Sliding Block Bearings
The bearing steel slide block has a glossy surface, no burrs and no gaps, and will not damage the guide rail or workpiece during use.
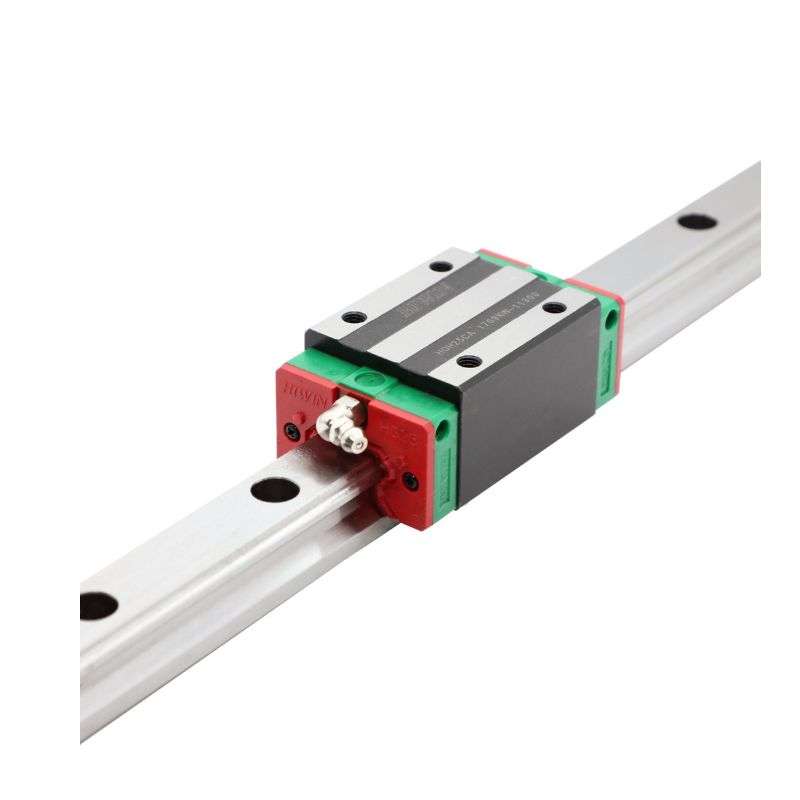

Sliding Block Bearings
This linear guide set consists of 2 guideway shafts and 4 industry standard bearing slides. The sliders are used in conjunction with the guideways and the internal linear bearings ensure smooth sliding. The shafts of the linear slides are made of high quality carbon steel and the bearing housings are made of aluminum alloy for durability.
Applications of Sliding Block Bearings

- Bridge Construction: Sliding block bearings are commonly used in the construction of bridges to allow for thermal expansion and contraction of the bridge’s structural components. They facilitate smooth movement and alignment of bridge sections, ensuring structural integrity over time.
- Large Machinery: Heavy industrial machinery and equipment, such as generators, turbines, and compressors, rely on sliding block bearings to support and align rotating components. These bearings can handle substantial loads and provide consistent performance, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Pipelines: In the oil and gas industry, pipelines need to accommodate ground settlement, temperature variations, and seismic activity. Sliding block bearings are used to support pipeline sections, allowing for controlled movement and reducing stress on the infrastructure.
- Turbines and Generators: Power generation facilities employ sliding block bearings in turbines and generators to maintain precise alignment and support the rotor shaft. These bearings enhance operational efficiency and minimize wear and tear.
- Railway Systems: Sliding block bearings are utilized in railway applications to support the smooth movement of tracks and bridges. They reduce friction and wear, contributing to the longevity of railway components and infrastructure.
- Dams and Hydropower Plants: Sliding block bearings are instrumental in the construction and operation of dams and hydropower plants. They allow for the controlled movement of sluice gates and other critical components, ensuring long-term functionality and stability.
- Building Construction: Large commercial and industrial buildings often incorporate sliding block bearings in their structural systems to accommodate building sway caused by wind or seismic activity. These bearings enhance occupant safety and reduce structural damage.
- Expansion Joints: In HVAC systems and piping networks, sliding block bearings are used in expansion joints to absorb thermal expansion and contraction, preventing stress and damage to the infrastructure.
- Shipbuilding: Sliding block bearings are essential in shipbuilding to support propeller shafts, rudders, and other components subjected to dynamic forces. They contribute to smooth navigation and reduce maintenance in marine applications.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Sliding block bearings find application in automotive assembly lines, particularly for conveyor systems, as they facilitate the smooth and controlled movement of vehicle chassis during production.
Key Manufacturing Process of Sliding Block Bearings
Material Selection
The process begins with the careful selection of materials. Common materials for sliding block bearings include bronze, stainless steel, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), or other self-lubricating materials. The choice of material depends on the specific application and environmental conditions.
Casting or Machining
The chosen material is either cast or machined to create the initial shape of the sliding block bearing. Casting is often used for larger bearings, while smaller bearings may be machined from solid stock. The goal is to achieve the desired dimensions and initial geometry.
Quality Control and Inspection
Comprehensive quality control and inspection processes are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. This includes dimensional checks, material analysis, and surface quality assessments to ensure the bearings meet the specified tolerances and standards.
Coating and Corrosion Protection
Depending on the application and material used, sliding block bearings may be coated or treated to provide corrosion resistance. This is especially important for outdoor or marine applications where exposure to harsh environmental conditions is likely.
Packaging and Labeling
Once the bearings have passed all quality checks and testing, they are packaged appropriately, often with protective materials, and labeled with essential information such as part numbers, specifications, and usage instructions.
Shipping and Distribution
The finished sliding block bearings are then ready for shipping to distributors, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), or end-users for integration into their industrial systems.


FAQ - Frequently Asked Questions

A slider bearing is a type of plain bearing that facilitates smooth sliding motion between two surfaces, typically using a low-friction material to reduce wear and friction.
Slider bearings are commonly used in industrial machinery, automotive systems, and various mechanical applications to support and guide moving parts.
Slider bearings can be made from materials like bronze, plastic, or composite materials to provide the necessary friction and wear characteristics for specific applications.
Selecting the right slider bearing involves considering factors such as load capacity, speed, temperature, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance.
Slider bearings typically require periodic lubrication to reduce friction and wear, but the maintenance schedule may vary depending on the application and bearing material.
Slider bearings can be designed to handle various loads, but their load capacity depends on factors like size, material, and design.
Yes, self-lubricating slider bearings use embedded lubrication materials or coatings to minimize the need for external lubrication.
Slider bearings offer advantages like simplicity, reduced cost, higher load capacity, and suitability for oscillating or slow-speed applications.
The performance of slider bearings in high-temperature environments depends on the material chosen; some materials are better suited for elevated temperatures.
Yes, manufacturers often offer customized slider bearings tailored to specific requirements, including size, shape, and material to meet the needs of diverse industries.
Installation and Maintenance of Sliding Block Bearing
Installation
Surface Preparation:Ensure that the mounting surfaces are clean, smooth, and free from contaminants to prevent premature wear.Remove any burrs or imperfections that may interfere with the bearing’s operation.
Lubrication:Depending on the type of slider bearing, apply a suitable lubricant or grease to the bearing surface or mating parts.Be cautious not to over-lubricate, as excess lubrication can attract debris and lead to increased wear.
Alignment:Properly align the bearing with the load to prevent misalignment issues that could cause premature failure.Follow manufacturer recommendations for alignment tolerances.
Securing:Secure the bearing in place using appropriate fasteners or housing components.Follow torque specifications to avoid damaging the bearing or fasteners.
Monitoring:After installation, check for any unusual noise, friction, or heat during the initial operation. Address any issues promptly.
Maintenance:
Regu larInspection:Periodically inspect slider bearings for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment.Look for changes in operating conditions, such as increased temperature or noise, which may indicate issues.
Lubrication Maintenance:Follow the recommended lubrication schedule provided by the manufacturer.Use the appropriate lubricants compatible with the bearing material and application conditions.
Cleaning:Keep the surrounding area free from dust, debris, and contaminants that can accelerate wear.Clean the bearing and its housing as needed to maintain optimal performance.
Replacement:If a slider bearing shows excessive wear or signs of damage, replace it promptly to prevent further damage to the machinery.
Environmental Considerations:Be mindful of the operating environment, especially in extreme conditions like high temperatures or corrosive atmospheres.Choose slider bearing materials that are suitable for the application’s environmental demands.
Training and Documentation:Ensure that maintenance personnel are adequately trained on slider bearing installation and maintenance procedures.Maintain records of maintenance activities and schedules for reference.

Related Posts
The Science Behind Friction Reduction in Slider Bearings
Categories The Science Behind Friction Reduction in Slider Bearings Table...
Read MoreSliding Block Bearings: The Unsung Heroes of Machinery
Sliding Block Bearing: The Unsung Heroes of Machinery Table of...
Read MoreSliding Block Bearings: Unlocking Efficiency in Machinery
Sliding Block Bearings: Unlocking Efficiency in Machinery Table of Contents...
Read More

