Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (28)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
How To Deal With When The Bearing Race Is Loose?
Introduction
When dealing with machinery and equipment, it is common to encounter malfunctioning issues such as loose bearing race. Loose bearing race can lead to a variety of problems, including increased friction, unusual noise, and ultimately even equipment failure. When encountering these problems is the case, how should we deal with it?
What Is A Bearing Race?
A bearing race is used to support and guide the rolling elements (such as balls or rollers) in a bearing in rotational motion. It usually consists of an inner ring and an outer ring, where the inner ring is connected to the shaft (or housing) and the outer ring is connected to an external structure (e.g., the housing). Bearing race is primarily designed to provide a smooth surface on which rolling elements can move to minimize friction and wear, and to convert axial loads into radial loads.
Bearing race must have sufficient hardness, surface smoothness and geometric accuracy to ensure that the bearing assembly will roll steadily during operation while minimizing energy loss and vibration. Typically, the surface of the bearing race is precision ground or ground and bored to achieve a high degree of flatness and roundness to ensure the stability and reliability of the bearing assembly.
In practice, bearing race must also withstand a variety of challenges from the external environment and operating conditions, such as high speeds, heavy loads, high temperatures, corrosion and contamination. Therefore, the selection of appropriate materials and surface treatments, as well as effective lubrication and sealing measures, are critical to extending the life of bearing races and improving bearing performance.
Inner ring
The bearing inner ring is an annular component that is usually mounted on a rotating shaft and serves as the raceway for the rolling elements of the bearing. It is designed to minimize friction and support the load of the rotating shaft. Usually made of high-quality steel or other durable materials and precision machined to ensure smooth operation of the bearings
Outer ring
The bearing outer ring is the outer part of the bearing that holds the bearing together and provides support for the rotating components within the bearing. Typically made of metal, it is the larger of the two rings in the bearing and is designed to fit securely into the bearing housing or mounting surface.
What Is The Function Of Bearing Race?
- The bearing race provide support and guide the rolling elements in the bearing in their rotary motion.
The rolling elements roll on the bearing race so that the entire bearing can effectively withstand the various forces and loads from the external environment and operating conditions.
- The surfaces of the bearing race usually have a high degree of flatness and roundness, as well as a smooth surface. Such a design reduces the friction between the rolling elements and the bearing race, thereby reducing energy loss and wear and extending the service life of the bearings.
- The bearing race are not only able to withstand loads from the axial direction, but can also switch the direction of loads.
This enables the bearing to withstand forces from different directions at the same time and maintain stable operation.
- High-quality bearing race design can improve the performance of the bearing;
This includes increasing its load capacity, reducing vibration and noise, and increasing axial rigidity.
- Bearing race also transmit power and torque.
The movement of the rolling elements on the race enables the bearing to effectively transmit rotational power and withstand the corresponding torque, thus realizing the normal operation of mechanical equipment.
How Bearing Race Should Be Assembled
- First of all, before assembling the bearing race, make sure that the race is free from damage and contamination; apply an appropriate amount of lubricant on their surfaces and on the parts in contact with the rolling elements, which can reduce friction and minimize wear during assembly.
- Install the inner ring and rolling elements; place the inner ring of the bearing in the mounting position to ensure that it fits well with the shaft. Then, place the rolling elements (e.g. balls or rollers) on the inner ring and ensure that they are evenly distributed in the bearing race.
- Mount the outer ring; place the outer ring of the bearing carefully on the inner ring and rolling elements and ensure that it is correctly aligned with the bearing race.
- During assembly, the appropriate assembly force is very important. Apply the right amount of force to ensure a good fit between the bearing race and the shaft and external structure (e.g. housing), while avoiding excessive deformation or damage to the bearing assembly.
- After completing the assembly, check that it is correctly fitted and can rotate freely to ensure that there is no noise or abnormal vibration, and also check that the fasteners of the race and related components are correctly tightened.
- Label the installation date and mark the bearing type specification.
How To Deal With When A Bearing Race Is Loose?
When a bearing is replaced each time, the race on which it sits is replaced at the same time. This also ensures that the new bearing will last for a long time because the race wear normally when rotating on the mating surfaces provided by the new race.
When bearing race become loose, there are signs of it.
- Abnormal Noise — Often abnormal noises such as clicking and rubbing occur during operation.
- Increased friction — There is increased friction between bearing components, leading to overheating and premature wear.
- Vibration— Excessive vibration can indicate the presence of loose bearing races, affecting the overall performance and reliability of the equipment.
- Reduced Efficiency — Loose bearing races can affect the efficiency of the equipment, resulting in reduced productivity and increased maintenance costs.
How To Deal With
The first step is to determine the cause of the loose bearing race. It could be improper installation, wear, or damage to the bearing or surrounding components.
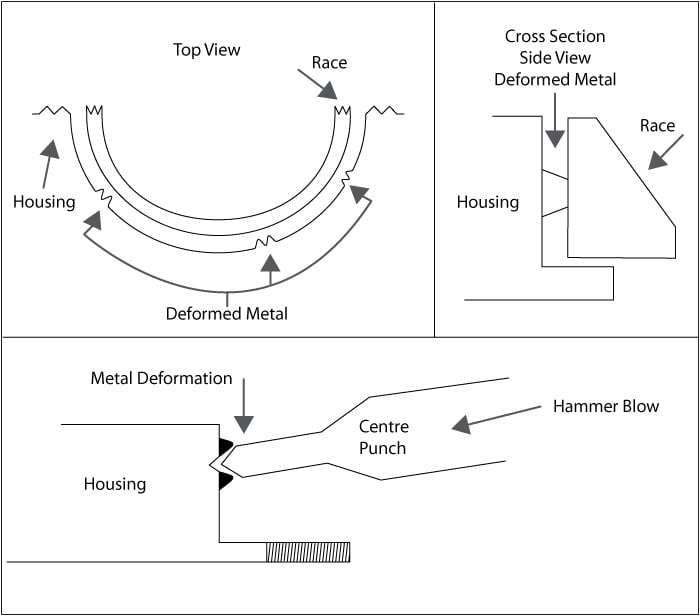
If bearing race looseness is caused by improper installation or a loose retaining nut, carefully tighten using the proper tools and torque specifications. Make sure not to over-tighten or damage may result.
Inspect the bearing race and surrounding components for any signs of wear, corrosion or damage. If any damage is found, replace the affected parts to ensure proper operation.
When bearing race remain loose even after tightening, consider fixing them with bearing adhesive.
If the bearing race are severely damaged please seek professional solutions.
Bearing Race Is Loose Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of bearing race is an important step in ensuring bearing performance and life.
First, perform regular visual inspections to check bearing race for abnormal wear, damage or contamination.
Next, regularly clean bearing race and related components and relubricate to minimize friction and wear.
Additionally, check bearing race for loose fasteners and ensure proper alignment of the bearings in their mounted position.
Test the bearings to see if they rotate smoothly and listen for any unusual noises that may indicate a problem with the race. Regular maintenance of bearing race helps prevent premature wear and ensures optimum bearing performance.
Finally, documenting the maintenance history and developing a proper maintenance program based on the manufacturer’s recommendations ensures that the bearing race is always in good condition and that identified problems are addressed in a timely manner to ensure stable operation and long-term reliability of the bearing system.
Conclusion
Bearing race is widely used in various mechanical equipment and industrial fields. Such as automobiles, aerospace, ships, power engineering, metallurgy, chemical industry, mining and other fields in the transmission system, rotating parts and motion devices.
The main purpose of bearing race is to support and guide the rolling elements for rotary motion, convert the direction of load, reduce friction and wear, and improve the performance and reliability of equipment.
Whether in high-speed mechanical equipment or in industrial applications under heavy-duty operating conditions, bearing race provide stable operation and long service life for a variety of applications.
Therefore, neglecting loose bearing race can lead to serious consequences. Loose bearing race increase friction and wear, leading to premature bearing failure and possible equipment failure and downtime. In addition, loose bearing race can generate abnormal noise and vibration, affecting the stability and reliability of the equipment, and may even lead to safety hazards. Therefore, timely detection and treatment of loose bearing race is essential to ensure the normal operation and safety of the equipment.
Bearing race is the tracks on which the rolling elements of a bearing (such as balls or rollers) move and have a direct impact on the efficiency, durability and performance of rotating equipment. Precision-machined race ensure smooth, consistent motion, minimize friction, reduce component wear, and maintain proper alignment within the bearing assembly. Ultimately, the quality and integrity of bearing race directly impacts the overall reliability and service life of machinery and equipment across a wide range of industries, making them a critical factor in engineering design and maintenance strategies.
References
- 1.Detailed explanation of ”bearing race“ from Wikipedia;
- 2.Additional information on ”bearing race“
- 3. Tips on fixing ”bearing race“.



















