Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (28)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
Rev Up with Confidence: A Guide to Camshaft Bearings

Introduction
Brief explanation of what camshaft bearings are
Camshaft bearings are crucial components in an internal combustion engine, serving to support and facilitate the smooth rotation of the camshaft. The camshaft plays a pivotal role in controlling the opening and closing of engine valves, determining the timing and duration of combustion events. Camshaft bearings are positioned within the engine block and provide a stable surface for the camshaft to rotate, reducing friction and wear. Typically made from materials like bronze or babbitt, these bearings ensure precise camshaft movement, enhancing overall engine performance and longevity by minimizing the impact of friction and stress on critical engine components.
Importance in Engine Performance
Camshaft bearings play a pivotal role in optimizing engine performance by providing crucial support to the camshaft, a key component in the internal combustion process. The camshaft dictates the precise timing and duration of valve movements, influencing combustion efficiency and power output. Camshaft bearings, positioned within the engine block, are instrumental in maintaining the camshaft’s rotational integrity. By reducing friction and wear, they ensure smooth camshaft operation, preventing potential damage and ensuring precise valve control. This not only enhances overall engine efficiency but also contributes to longevity and reliability. The proper functioning of camshaft bearings is essential for achieving optimal combustion, power delivery, and fuel efficiency in internal combustion engines.
Anatomy of a Camshaft Bearing
Definition and function of a camshaft bearing
Camshaft bearings are a crucial component in the valvetrain system of an internal combustion engine, designed to provide support and reduce friction for the camshaft. The camshaft is responsible for actuating the engine’s intake and exhaust valves, ensuring the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the expulsion of exhaust gases. To achieve this, the camshaft must rotate smoothly and with high precision, which is where camshaft bearings come into play. These bearings act as a buffer between the rotating camshaft and the stationary engine block, minimizing friction and wear while also maintaining the camshaft’s alignment. Constructed from materials such as steel or bronze, camshaft bearings are designed to withstand high loads and temperatures. Proper lubrication is key to maintaining the health of camshaft bearings, as it reduces friction and prevents overheating. In summary, camshaft bearings play a vital role in the valvetrain system by facilitating the smooth rotation of the camshaft, ensuring the efficient operation of the engine.
Different types of camshaft bearings
Journal Bearings (Plain Bearings): These bearings consist of a smooth cylindrical surface that supports the camshaft. They are often made of materials like bronze or babbitt, and the interface between the camshaft and the bearing relies on a film of lubricating oil. Journal bearings are widely used due to their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and effectiveness in minimizing friction.
Roller Bearings: In contrast to journal bearings, roller bearings employ small cylindrical rollers between the camshaft and the bearing surface. This design reduces point contact and distributes the load more evenly, resulting in lower friction and increased durability. Roller bearings are often preferred in high-performance and racing engines where the demand for precision and reduced friction is critical.
Needle Bearings: Needle bearings utilize cylindrical rollers with a high length-to-diameter ratio, resembling needles. This design enhances the load-carrying capacity and efficiency of the bearing. Needle bearings are particularly suitable for applications with high radial loads, providing improved support to the camshaft in challenging operating conditions.
Flanged Bearings: These bearings feature an extended lip or flange on one or both sides. The flange aids in proper alignment and helps stabilize the camshaft within the engine. The extended surface also provides additional support against lateral movement, contributing to the overall reliability and longevity of the camshaft. Flanged bearings are commonly used in engines where precise alignment is crucial to prevent premature wear and ensure optimal performance.
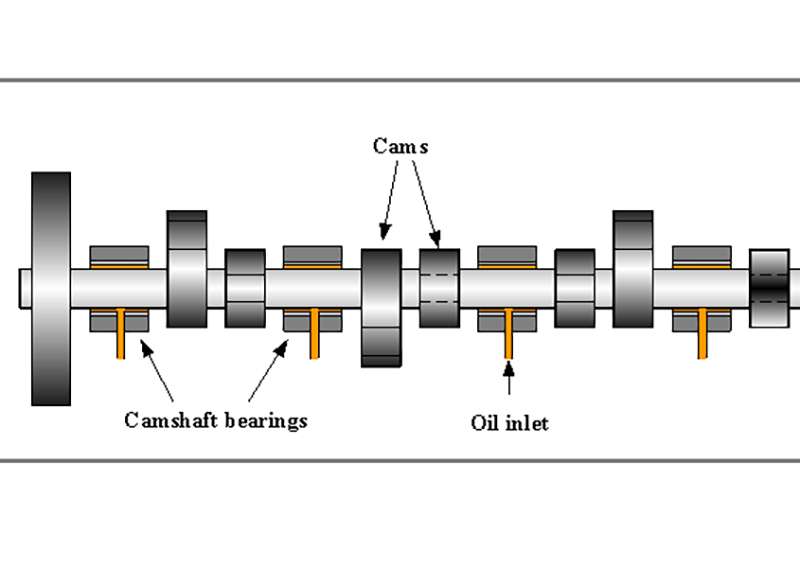
Components of a camshaft bearing
Camshaft bearings consist of essential components designed to support and facilitate the smooth rotation of the camshaft within an internal combustion engine. The primary element is the bearing shell or sleeve, providing the surface against which the camshaft rotates. These bearings can be plain (journal), incorporate rollers (roller bearing), or utilize needle-like cylindrical rollers (needle bearing). Typically crafted from materials like bronze or babbitt, the bearings also include lubrication channels for optimal oil distribution, ensuring a protective film between the bearing and camshaft to minimize friction. In variations like flanged bearings, an extended lip enhances stability, while roller and needle bearings feature additional components such as rollers and cages for improved load distribution and efficiency.
How Camshaft Bearings Work
As the engine operates, the camshaft, a centrally positioned shaft, orchestrates the precise opening and closing of the engine valves, influencing the timing and duration of combustion events. The camshaft bearings, strategically positioned within the engine block, create a smooth and low-friction interface for the camshaft to rotate. These bearings can take various forms, such as plain journal bearings, roller bearings, or needle bearings, depending on the design and performance requirements of the engine. Importantly, the bearing surfaces are lubricated by oil channels, forming a protective film that minimizes friction and wear. This lubrication is crucial for preventing metal-to-metal contact and ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of both the camshaft and the bearings. In essence, camshaft bearings work by providing stable support and reducing friction, allowing the camshaft to execute its vital role in controlling valve movements and optimizing the combustion process within the engine.
Importance of proper alignment of the camshaft and bearings
Alignment ensures that the camshaft rotates smoothly within the bearings, minimizing friction and wear. When the camshaft is correctly aligned, it optimally controls the opening and closing of engine valves, determining the timing and duration of combustion events. Misalignment can lead to increased friction, premature wear on the camshaft and bearings, and a potential decrease in engine performance. It may also result in inefficient valve timing, affecting combustion efficiency and overall power delivery. Additionally, proper alignment contributes to the longevity of the engine components, reducing the likelihood of premature failures and ensuring consistent and reliable engine operation. In summary, the alignment of the camshaft and bearings is critical for maintaining optimal engine performance, minimizing wear, and maximizing the lifespan of internal combustion engines.
Factors That Affect Camshaft Bearing Life
Quality of the camshaft bearing material
The quality of camshaft bearing materials significantly influences the lifespan and performance of these crucial engine components. High-quality materials, such as durable alloys or precision-engineered babbitt, enhance bearing strength and wear resistance. Properly chosen materials can withstand the rigors of constant friction and load, reducing the likelihood of premature wear and deterioration. Additionally, advanced materials contribute to improved heat dissipation, crucial in high-performance engines where temperature management is vital. Investing in top-tier materials for camshaft bearings ensures that they maintain their structural integrity over time, withstand the demands of the engine environment, and contribute to overall reliability. In contrast, lower-quality materials may result in accelerated wear, increased friction, and compromised engine performance, emphasizing the pivotal role that material quality plays in determining camshaft bearing longevity.
Operating temperature and load conditions
Elevated temperatures, often encountered during extended periods of high-speed or heavy load operation, can lead to accelerated wear and thermal stress on the bearings. Adequate lubrication is essential to mitigate these effects, as it helps dissipate heat and reduce friction. Moreover, extreme load conditions, such as those experienced in high-performance engines or heavy-duty applications, put additional strain on the camshaft bearings. Continuous exposure to excessive loads may lead to premature wear, deformation, or failure of the bearings. Proper design considerations, effective lubrication systems, and suitable materials are essential to ensure that camshaft bearings withstand varying temperature and load conditions, contributing to prolonged operational reliability and enhanced engine performance.
Quality and frequency of maintenance
Regular and meticulous maintenance practices directly impact the bearing’s ability to withstand the demanding conditions within the engine. High-quality maintenance involves adhering to recommended oil change intervals, ensuring the use of quality lubricants, and conducting routine inspections. Proper lubrication is paramount, as it forms a protective barrier between the camshaft and bearings, reducing friction and preventing premature wear. The timely replacement of oil filters and the careful monitoring of oil levels contribute to an environment that promotes optimal bearing function. Regular inspections provide an opportunity to identify early signs of wear, misalignment, or other issues, enabling corrective action before problems escalate. Conversely, neglecting maintenance introduces the risk of inadequate lubrication, the buildup of contaminants, and compromised bearing integrity, potentially leading to costly repairs and reduced engine efficiency. In essence, a proactive and high-quality maintenance approach is essential for ensuring the prolonged and reliable performance of camshaft bearings.

Symptoms of Worn or Damaged Camshaft Bearings
Increased Engine Noise: One noticeable symptom of camshaft bearing wear or damage is an increase in engine noise. As the bearings deteriorate, they may produce a distinctive knocking or ticking sound, indicating friction and reduced efficiency in the camshaft’s rotation.
Poor Engine Performance: Wear or damage to camshaft bearings can negatively impact engine performance. Reduced support for the camshaft can lead to improper valve timing, resulting in decreased power, sluggish acceleration, and overall diminished engine efficiency.
Low Oil Pressure: Camshaft bearings rely on adequate lubrication for smooth operation. Wear or damage can compromise the lubrication system, leading to lower oil pressure. Monitoring oil pressure is crucial, as a significant drop may indicate issues with the camshaft bearings.
Excessive Vibration: Damaged camshaft bearings can cause increased vibration in the engine. This vibration may be felt through the vehicle’s structure or noticed as a rough idling sensation. It suggests a lack of stability in the camshaft’s rotation.
Visible Metal Shavings in Oil: During routine oil changes, inspecting the drained oil for metallic particles or shavings can reveal potential camshaft bearing issues. Excessive wear or damage may cause the bearings to shed metal particles into the oil, indicating the need for further investigation and potential bearing replacement.
Diagnosis of Camshaft Bearing Issues
Diagnosing camshaft bearing problems involves a combination of visual inspections, listening for unusual sounds, and utilizing specialized tools. Visual inspection during routine maintenance involves examining the engine’s components for signs of wear, including the camshaft bearings. The presence of metal shavings or debris in the oil during an oil change can indicate bearing deterioration. Listening for abnormal engine noises, such as knocking or ticking sounds, especially during acceleration or deceleration, can point to potential camshaft bearing issues. Utilizing tools like a stethoscope or a mechanic’s stethoscope can help pinpoint specific areas of concern by listening to the engine while it’s running. Monitoring oil pressure using a gauge during operation can also provide valuable information, as a drop in pressure may indicate problems with the camshaft bearings. Combining these methods allows for a comprehensive assessment of camshaft bearing health, facilitating early detection and timely intervention to prevent further damage and ensure optimal engine performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, camshaft bearings are indispensable components in internal combustion engines, supporting the camshaft’s rotation and optimizing valvetrain performance. Their crucial role in reducing friction, ensuring proper alignment, and enhancing engine efficiency underscores their impact on overall reliability and longevity. Various types of camshaft bearings cater to diverse engine requirements, with factors like material quality, operating conditions, and maintenance practices influencing their lifespan. Recognizing symptoms of wear and employing effective diagnostic methods are essential for timely intervention. Ultimately, the meticulous care and consideration given to camshaft bearings contribute significantly to sustained engine health and performance.
References
- 1.”Camshaft Bearings” from Advance Auto Parts;
- 2. “Camshaft Bearings” from Enginetech;
- 3. “Camshaft Bearings” from Engine Parts Canada.


















