Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (28)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
How To Choose The Right Circlip For Your Project: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In mechanical assembly, Circlip is mainly used to fix bearings, gears, shafts, and other rotating parts to ensure that these parts operate safely at predetermined positions and prevent failures caused by axial movement. In addition, the use of Circlip helps simplify the assembly process, improve production efficiency, and reduce manufacturing costs.
Circlip mainly achieves its function through mechanical pressure. When the Circlip is installed in the preset groove of the shaft or hole, its inner and outer diameters will be in close contact with the shaft or hole wall, providing the necessary clamping force through elastic force or tension to lock or position other components of the assembly.
What Is Circlip
A circlip, also known as a retaining ring or snap ring, is a fastener or mechanical component typically used to secure other components to a shaft or within a hole (housing). The primary function of a retaining ring is to restrict component movement along the axis of a shaft or cylindrical assembly, thus preventing disassembly or unwanted movement.
It is usually C-shaped or round in shape with a small gap or opening. By fitting into the groove, the circlip provides a shoulder to secure the assembled parts so that it does not shift when the parts need to be rotated or moved together.
Materials For Circlip
circlips are made from a variety of materials, each selected for their specific properties such as elasticity, strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness :
1.Spring steel: It is the most commonly used material for circlips. Due to its excellent elasticity and resilience, it is mostly used in industrial machinery.
2. Stainless steel: It has good rust and corrosion resistance and is suitable for use in harsh environments such as marine, food processing, and medical applications.
3. Carbon Steel: Has high strength, but is less corrosion-resistant than stainless steel and may require protective coatings. It should be selected for applications where cost is more important than corrosion resistance.
4. Alloy steel: It can be heat-treated to improve strength and wear resistance. Typically used in retaining rings requiring extra strength and resistance to environmental stresses.
5. Phosphor bronze: It has excellent corrosion resistance and low spark risk, and is suitable for electrical equipment.
6. Inconel: It has high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, and is generally suitable for aerospace and nuclear applications.
7. Plastics: Plastics such as nylon are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and non-conductive and are used when non-metallic properties are required, such as electrical insulation or corrosion resistance beyond what metals can provide.
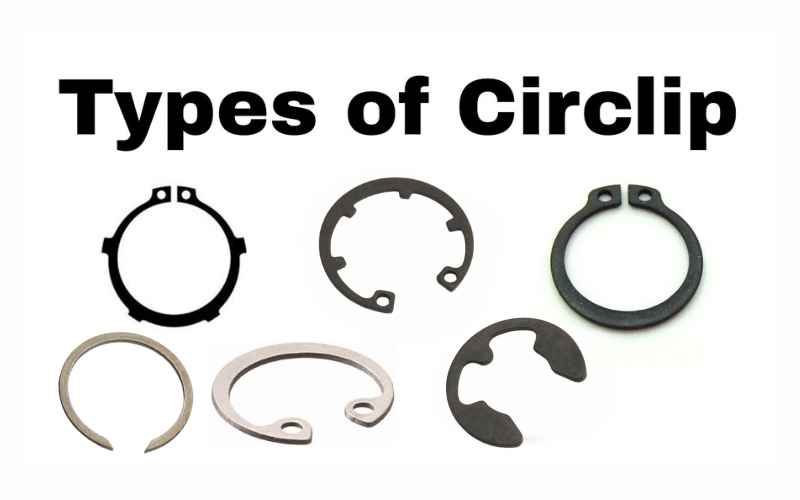
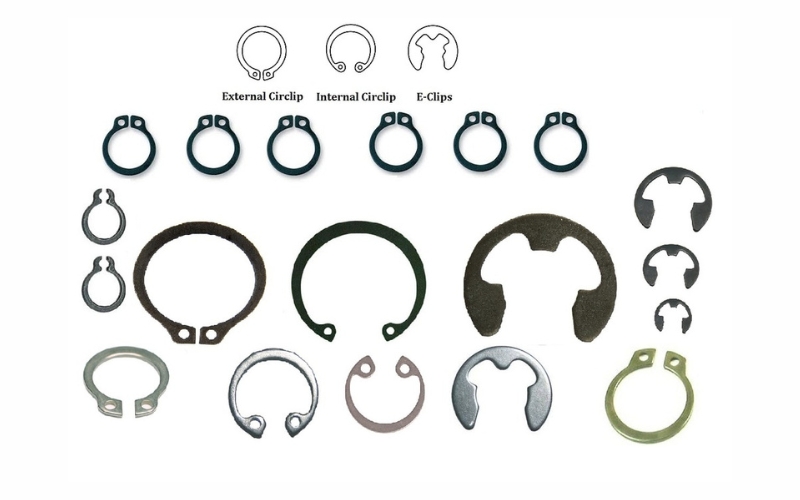
Basic Types Of Circlip
Circlips come in several types, each with different shapes and characteristics:
- External Circlip Standard
This is the most common type of circlip, designed to be fitted onto the outside of a shaft.
Features: It has a simple, open-ended C-shape that snaps into a groove on the shaft.
- External Circlip Lugged
Similar to the standard external circlip but features lugs (small extensions or tabs).
Features: The lugs facilitate easier removal and installation, often allowing the use of special tools that engage these lugs for more controlled operation.
- Internal Circlip Standard
They are designed for installation inside a bore or housing.
Features: This circlip has a gap-shaped C-shape, allowing it to contract and fit into a groove within a bore, exerting inward pressure.
- Internal Circlip Lugged
An internal circlip that includes lugs.
Features: The lugs provide leverage points for specialized tools, making installation and removal easier, especially in tight spaces where traditional circlip tips might be hard to grasp.
- E Type External Circlip
An external circlip that resembles the letter “E.”
Features: Typically has three prongs that provide a secure fit, making installation straightforward without the need for a groove.
- Stainless Steel Circlip
Stainless Steel Circlip is one of the most commonly used materials for making Circlips.
Features: Stainless steel is tough and durable, allowing the Circlip to be used for a long time after installation.
- Snap Rings
A broad category of retaining rings, snap rings are similar to standard circlips but can vary in design.
Features: They usually feature a simple, flat, or slightly rounded ring design without lugs, designed to snap into place.
What Are They Used For?
Circlips are versatile components used in various mechanical and engineering applications to secure parts in place. Here are some common uses for circlips:
- Securing Bearings: Automotive wheel hubs, electric motors, and gearboxes.
- Axle and Shaft Retention: Automotive axles, industrial machinery, and bicycle wheel assemblies.
- Assembling Mechanical Components: Consumer electronics, appliances, and power tools.
- Limiting Movement: Slides, guides, and pistons in hydraulic or pneumatic systems.
- Preventing Leakage: Hydraulic cylinders and air compressors.
- Maintaining Assembly Alignment: Optical devices, precision instruments, and assembly fixtures.
Circlips are chosen for their simplicity, effectiveness, and ease of installation, making them a preferred choice for many mechanical retention tasks.
Advantages Of Circlip
Circlips offer a number of advantages in mechanical design and assembly. Here are some key benefits:
- Cost-effective
- Ease of Installation
- Space Efficiency
- Provides a secure, durable retention mechanism
- Versatility
- Long service life and low probability of deformation
- No additional fastening hardware is required, reducing the complexity
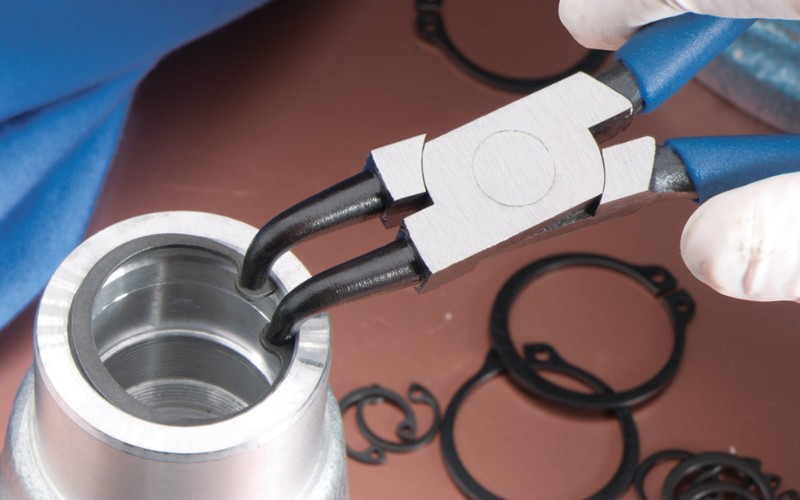
How To Install A Circlip
How To Install External Circlips
Installing External Circlips requires precision and great care to ensure they fit securely onto the shaft. Start by selecting the appropriate size of Circlips for the shaft, making sure the diameter of the Circlips is slightly larger than the diameter of the shaft for a tight fit. Start by inserting the tips of pliers into the small holes on each end of the Circlip and squeezing the handles together, causing the Circlip to expand. Then carefully place the Circlips close to the groove in the shaft where they will fit. Make sure the opening of the Circlips is vertically aligned with the axis of the shaft, and slowly release pressure on the clamp handle to allow the Circlips to retract and fit into the grooves on the shaft. If necessary, tap a few times with a soft-faced hammer to make sure the Circlips are fully seated in the grooves. Finally, visually inspect the installation to confirm that the Circlips are evenly and securely seated in place, with no parts hanging out of the grooves.
How To Install Internal Circlips
Installing Internal Circlips requires inserting the Circlips into a hole or a groove within the housing. First, select an Internal Circlip that closely matches the diameter of the hole. Be careful to ensure that the Circlip is slightly larger than the hole to achieve a tight fit. Use a pair of reverse-action circlip pliers that work in the opposite direction to those used for external circlips; these pliers compress the Circlips when the handle is squeezed. Start by compressing the Circlip with pliers, aligning the tip of the pliers with the hole or notch in the end of the Circlip. Insert the compressed Circlips into the holes so they line up with the grooves inside the housing. Slowly loosen the plier handle so that the Circlips spread out and fit snugly into the groove. If necessary, use a small flat-blade screwdriver or similar tool to adjust the Circlips and ensure they seat evenly.

Size And Fit
Circlip Sizes Measurement Standards
Circlips are standardized according to different regional and international standards, which define their dimensions and tolerances. Some common standards include:
DIN 471 and DIN 472: These are German standards for external and internal circlips, respectively, and are widely used in engineering worldwide.
ANSI B27.7: American standard for retaining rings, detailing requirements, and sizing for circlips used in various applications.
ISO 3601: International standard that provides dimensions and specifications for circlips among other sealing devices.
When selecting a circlip, it is crucial to consider the operating environment and the mechanical loads it will face. The material, size, and type of circlip must be appropriate to ensure it functions effectively without failing or causing damage to the assembly.
Precise Fit And Consequences Of Improper Sizing
Precise fitting is crucial in the installation of mechanical components, especially when using positioning parts like circlips. Choosing the appropriate size ensures that the circlips can effectively bear the intended load and keep components securely in place, thus ensuring the normal operation and safety of mechanical equipment. If the size of the circlips is too large or too small, it may lead to equipment failure.
Circlips that are too large may not fit correctly into the designated groove, causing components to move or detach during mechanical operation, increasing wear and possibly leading to machine downtime. Additionally, overly large circlips might deform or get damaged during forced installation, which could also damage the groove or shaft itself.
Conversely, circlips that are too small may be too tight during installation, making the installation difficult, and over time, such circlips might break due to metal fatigue or excessive stress. This too can cause components to become loose or detach.
Therefore, selecting the right size of circlips and ensuring their precise fit is essential. This not only affects the efficiency of the equipment’s operation but also relates to maintenance costs and the extension of the equipment’s lifespan. When designing and maintaining mechanical equipment, it is crucial to choose and install circlips strictly according to the manufacturer’s specifications to avoid a range of problems caused by inappropriate sizing.
References
- 1. Introduction to the types of” circlips “from Barnwell Company
- 2. A Complete Guide to “Circlips” from RS




















Hі there! Do y᧐u use Twittеr? I’d like
to follow you if that would be ok. I’m definitely enjoying
your blog and look forward to new upɗates.
Thank you! Yes, we are on Twitter. You can follow us here. Looking forward to connecting!
Very good info. Lucky me I recently found your website
by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve saved it for later!
Thank you! I’m glad you found it. Happy to hear you saved it for later!