Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (28)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
Effortless Motion: Embracing Self-Lubricating Plain Bearings
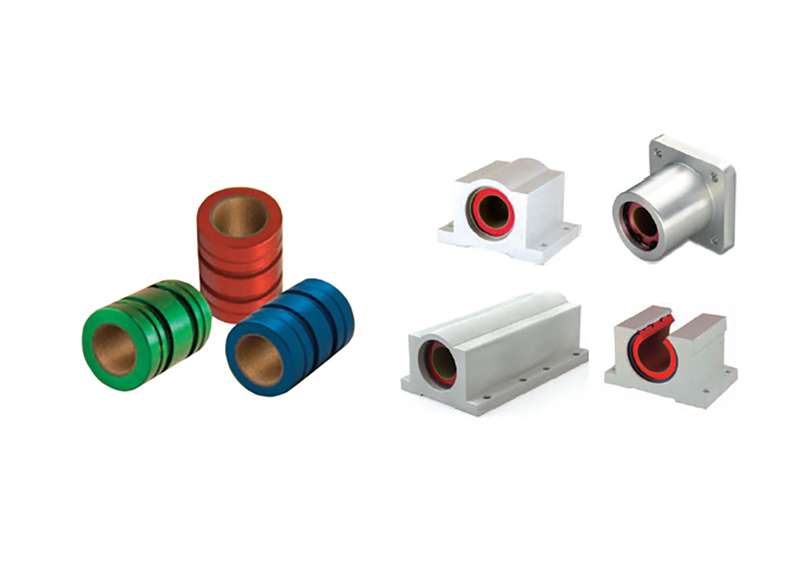

Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of bearing technology, a groundbreaking innovation has emerged—Self-Lubricating Plain Bearings. These extraordinary components revolutionize motion control by obviating the necessity for external lubrication, presenting an array of advantages across diverse applications. This exploration delves into the realm of self-lubricating bearings, elucidating their transformative impact on industries.
Definition of Self-Lubricating Plain Bearings
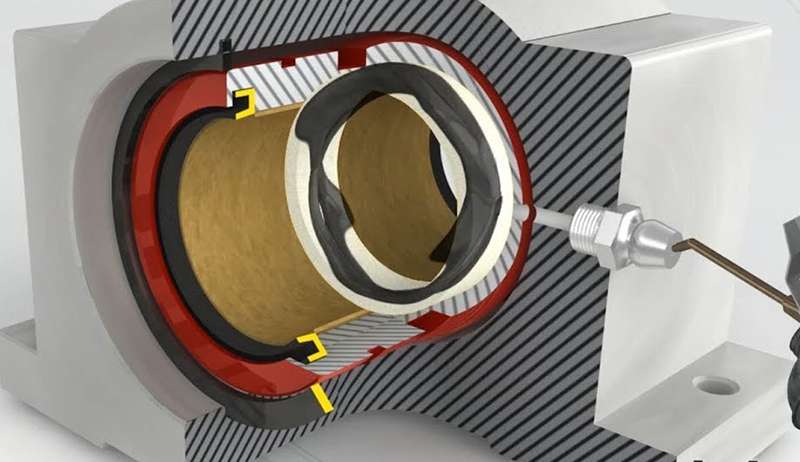
Self-lubricating plain bearings, also known as bushings or sleeve bearings, epitomize a technological leap by seamlessly operating without the dependence on supplementary lubrication. Unlike traditional bearings, which demand frequent greasing or oiling, self-lubricating variants intricately integrate solid lubricants into their structural composition, ensuring an operation that is not only maintenance-free but also highly efficient.
How Self-Lubricating Bearings Work
Self-lubricating sliding bearings operate on a sophisticated principle that combines carefully chosen material composition with integrated lubrication mechanisms. The bearings incorporate solid lubricants like graphite or PTFE into their composition, imparting inherent low-friction properties to the material. These lubricating elements act as reservoirs within the bearing structure. As the bearing experiences movement, the embedded lubricant is gradually released, forming a consistent lubricating film between the sliding surfaces. This film not only reduces friction but also minimizes wear and heat generation. The integration of lubrication within the bearing eliminates the need for external lubrication sources, making self-lubricating sliding bearings particularly advantageous in applications where regular maintenance is challenging. This dual approach of specialized material composition and embedded lubrication ensures prolonged efficiency and reliability in various industrial contexts.
Advantages of Self-Lubricating Plain Bearings
Maintenance-Free Operation: One of the primary advantages of self-lubricating sliding bearings is their ability to operate without the need for external lubrication. This feature significantly reduces maintenance requirements and associated downtime.
Extended Service Life: The embedded solid lubricants, such as graphite or PTFE, create a consistent and protective film between sliding surfaces. This minimizes friction and wear, contributing to a longer service life for the bearing compared to traditional bearings.
Cost-Efficiency: The reduced need for maintenance and the extended lifespan of self-lubricating sliding bearings result in cost savings over time. Industries benefit from lower maintenance costs and decreased downtime, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Versatility in Applications: Self-lubricating sliding bearings are well-suited for a wide range of applications, including those with challenging environmental conditions or limited access for regular maintenance. Their adaptability makes them suitable for diverse industrial settings.
Improved Performance: These bearings offer improved performance due to the continuous and reliable lubrication provided by the embedded solid lubricants. This results in smoother operation, reduced heat generation, and enhanced overall efficiency in various mechanical systems.
Applications of Self-Lubricating Plain Bearings
Automotive Industry: Self-lubricating sliding bearings find widespread use in the automotive sector, particularly in components like suspension systems, steering columns, and gearbox mechanisms, where their low-maintenance and durable characteristics contribute to improved performance and longevity.
Aerospace Applications: In the aerospace industry, self-lubricating sliding bearings are employed in critical components such as aircraft landing gear, control surfaces, and actuators. Their ability to operate without frequent maintenance makes them valuable in the demanding conditions of aerospace systems.
Industrial Machinery: Various types of industrial machinery, including conveyor systems, pumps, and manufacturing equipment, benefit from the self-lubricating properties of these bearings. The reduced need for manual lubrication enhances the reliability and efficiency of industrial processes.
Marine Equipment: Self-lubricating sliding bearings are utilized in marine applications, such as ship propeller shafts and rudder systems. Their resistance to water and ability to withstand harsh marine environments make them suitable for use in maritime equipment.
Renewable Energy Systems: Wind turbines and solar tracking systems incorporate self-lubricating sliding bearings to minimize maintenance requirements and ensure reliable operation. These bearings contribute to the efficiency and sustainability of renewable energy infrastructure.
Medical Devices: In medical equipment, particularly in precision instruments and imaging devices, self-lubricating sliding bearings provide smooth and reliable movement. Their low-friction properties and maintenance-free operation are advantageous in healthcare applications requiring precision and reliability.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper Installation Procedures
Clean and Inspect Surfaces: Before installation, ensure that the mating surfaces are clean and free from any contaminants or debris. Inspect both the shaft and the housing to guarantee a smooth and proper fit for the self-lubricating sliding bearing.
Proper Alignment: Ensure precise alignment of the bearing with the mating components, such as the shaft and housing. Misalignment can lead to uneven stress distribution and premature wear, compromising the performance of the self-lubricating sliding bearing.
Avoid Distortion: During installation, take care to avoid any distortion or damage to the bearing. Use appropriate tools and techniques to prevent excessive force that may deform or harm the bearing material.
Avoid Impact and Shock: Handle the self-lubricating sliding bearing with care to prevent any impact or shock during installation. Sudden force can damage the bearing structure or displace the embedded lubricating elements.
Ensure Proper Tolerance: Confirm that the shaft and housing tolerances are within the recommended range for the specific self-lubricating sliding bearing. Incorrect tolerances can lead to improper fit, increased friction, and reduced bearing performance.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the installation guidelines provided by the bearing manufacturer. Different self-lubricating bearings may have specific requirements based on their design and materials, and following the manufacturer’s recommendations ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Maintenance Tips
Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect self-lubricating sliding bearings for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage. Visual checks can help identify issues early on, allowing for timely maintenance.
Address Misalignment: If misalignment is detected during inspection, take corrective measures promptly. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear and reduce the effectiveness of the self-lubricating properties.
Temperature Control: Be mindful of operating temperatures, as excessive heat can impact the performance of self-lubricating sliding bearings. Ensure that the bearings operate within the recommended temperature range to maintain their integrity and effectiveness.

Industry Trends and Innovations
The self-lubricating sliding bearing industry is witnessing significant trends and technological innovations aimed at enhancing performance, durability, and sustainability. One notable trend involves the development of advanced composite materials for bearing construction, offering improved strength, wear resistance, and reduced friction. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on the integration of smart technologies, such as sensors and monitoring systems, to enable real-time performance tracking and predictive maintenance. This proactive approach enhances overall reliability and reduces downtime. Furthermore, eco-friendly lubrication solutions, such as bio-based or dry lubricants, are gaining traction, aligning with the industry’s focus on environmental sustainability. Lastly, additive manufacturing techniques, like 3D printing, are being explored for customized and complex bearing designs, providing flexibility in production. These trends collectively signify a shift towards more efficient, environmentally conscious, and technologically advanced solutions in the self-lubricating sliding bearing industry.
Environmental Impact
On the positive side, these bearings can contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing the need for external lubrication, which minimizes the use of traditional lubricants that may contain harmful additives. The extended lifespan of self-lubricating bearings also results in less frequent replacements, reducing overall waste generation.
However, the negative impact lies in the production and disposal processes. The manufacturing of self-lubricating bearings may involve resource-intensive procedures and the use of materials with environmental implications. Additionally, the disposal of these bearings at the end of their life cycle may pose challenges, especially if the materials are not easily recyclable. Balancing these factors requires continuous innovation to improve the eco-friendliness of materials, production processes, and disposal methods in the self-lubricating sliding bearing industry.
Misconceptions about Self-Lubricating Plain Bearings
Misunderstandings about self-lubricating sliding bearings can arise due to various factors. One common misconception is that these bearings are completely maintenance-free. While they require less external lubrication, periodic inspection and monitoring are crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Another misunderstanding involves the assumption that all self-lubricating bearings are suitable for every application. In reality, the selection of bearings should align with specific operational requirements, load conditions, and environmental factors to maximize efficiency. Additionally, there may be misconceptions about the complexity of installation. While self-lubricating bearings offer advantages, proper installation procedures are essential to prevent issues such as misalignment or distortion. Addressing these misunderstandings requires clear communication of the capabilities and limitations of self-lubricating sliding bearings, promoting informed decision-making in their application and maintenance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the advent of self-lubricating plain bearings represents a transformative breakthrough in bearing technology, offering industries a maintenance-free and efficient solution. These bearings, incorporating solid lubricants, provide extended service life, cost-efficiency, and versatility across diverse applications—from automotive and aerospace to medical devices and renewable energy systems. Proper installation and regular maintenance are imperative for optimal performance. Industry trends focus on advanced materials, smart technologies, and eco-friendly lubrication, ushering in a new era of efficiency and sustainability. While self-lubricating bearings contribute to environmental sustainability, addressing production and disposal challenges remains crucial. Clearing misconceptions ensures informed decision-making, emphasizing the nuanced requirements of specific applications for these remarkable components.
References
1.”Plain bearing” from Wikipedia;
2. “The Science Of Self-Lubricating Plain Bearings” from PBC Linear;
3. “AMPEP self-lubricating spherical plain bearings” from SKF.


















