Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (28)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
Understanding Take-Up Bearings: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
Definition of Take-Up Bearings
Take-up bearings are mechanical components designed to accommodate the expansion and contraction of conveyor or drive system shafts due to variations in temperature or other factors. These bearings are commonly used in industrial applications where there is a need for adjustable positioning of the shaft. The take-up bearing assembly typically consists of a housing and a bearing unit that allows for axial movement, facilitating easy tensioning or loosening of the system. This adjustability is crucial for maintaining proper belt or chain tension in conveyor systems, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing wear on components. Take-up bearings play a vital role in supporting efficient and reliable operation of various mechanical systems in industrial settings.
Importance in Industrial Applications
Take-up bearings hold significant importance in industrial applications, providing a crucial solution for managing the dynamic factors affecting conveyor and drive system shafts. Their primary function is to absorb thermal expansion, vibrations, and other forces that lead to shaft movement. This adjustability ensures the proper tensioning of belts or chains, preventing slack and maintaining system integrity. By facilitating easy adjustment and accommodating fluctuations in operating conditions, take-up bearings contribute to the longevity of mechanical components and enhance overall system efficiency. Their role in mitigating wear and tear, reducing maintenance requirements, and optimizing performance underscores their essential place in ensuring the reliability and functionality of industrial machinery.
Functionality of Take-Up Bearings
Tension Adjustment: Take-up bearings facilitate the adjustment of tension in conveyor or drive systems, ensuring optimal tension in belts or chains by accommodating thermal expansion, contraction, or other factors.
Shaft Misalignment Support: Take-up bearings play a crucial role in supporting and compensating for shaft misalignment, helping to maintain proper alignment in industrial machinery and preventing excessive stress on the system.
Absorption of Thermal Expansion: These bearings absorb and manage the axial movement of shafts caused by thermal expansion, preventing issues related to temperature variations and promoting stable and efficient system operation.
Maintenance of System Integrity: By preventing slack and maintaining the appropriate tension in belts or chains, take-up bearings contribute to the overall integrity of industrial systems, reducing the risk of component failure and ensuring reliable operation.
Facilitation of Easy Adjustment: Take-up bearings are designed to allow for easy and accessible adjustment, simplifying maintenance procedures. This feature enables quick and efficient changes in tension levels as needed, promoting smooth and trouble-free operation of industrial machinery.
Types of Take-Up Bearings
There are various types of take-up bearings designed to meet specific industrial requirements. The five main types include:
Frame Type Take-Up Bearings: These are mounted within a frame structure and provide support for shaft adjustment. They are commonly used in conveyor systems and can accommodate both radial and axial loads.
Center Pull Take-Up Bearings: Featuring a pull-style design, these bearings allow for easy adjustment of tension by pulling the bearing housing towards the center. This type is suitable for applications where space constraints or specific mounting configurations exist.
Top Angle Take-Up Bearings: Designed with an angled top to facilitate shaft adjustment, these bearings are suitable for applications where the take-up unit needs to be mounted at an angle. They provide flexibility in addressing misalignment issues.
Wide-Slot Take-Up Bearings: These bearings have a wider inner ring to accommodate larger shaft movements and facilitate easier adjustment. They are ideal for applications where substantial thermal expansion or contraction is expected.
Side-Mount Take-Up Bearings: Mounted on the side of the frame or support structure, these bearings provide an alternative configuration for adjusting shaft tension. They are used in applications where top or center mounting is not practical or possible.
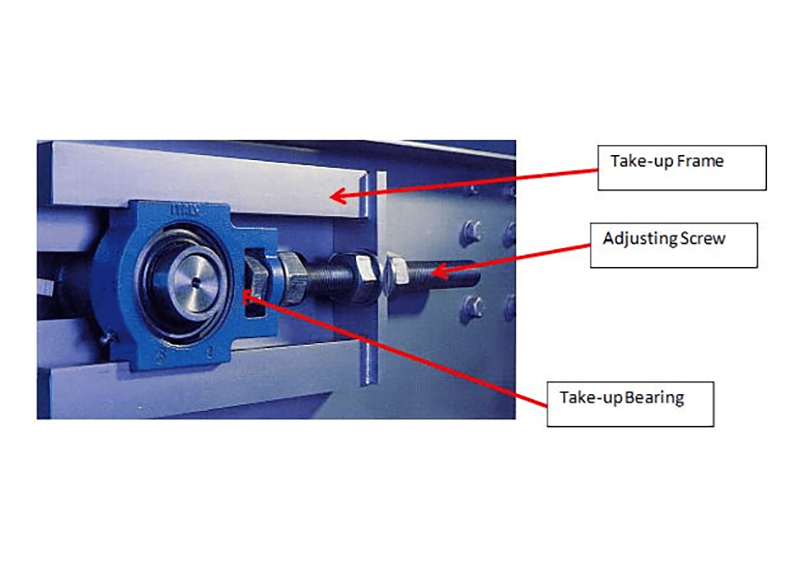
Design Features
Housing Styles
Take-up bearings exhibit diverse design features in their housing styles, catering to the specific demands of industrial applications. Frame Type Take-Up Bearings are characterized by their robust frame structure, providing stable support for shaft adjustment and accommodating both radial and axial loads efficiently. Center Pull Take-Up Bearings employ a pull-style design, allowing for straightforward tension adjustment by pulling the housing towards the center, making them suitable for applications with limited space or specific mounting constraints. Top Angle Take-Up Bearings feature an angled top, facilitating easy shaft adjustment and offering flexibility to address misalignment issues. Wide-Slot Take-Up Bearings stand out with a wider inner ring, enabling them to accommodate larger shaft movements and providing ease of adjustment in applications with substantial thermal expansion or contraction. Side-Mount Take-Up Bearings offer an alternative configuration, mounted on the side of the frame or support structure, providing practical solutions in cases where top or center mounting is not feasible. These varied housing styles showcase the adaptability and versatility of take-up bearings in meeting the dynamic needs of industrial settings.
Adjustability Mechanisms
Take-up bearings boast distinctive design features in their adjustment mechanisms, playing a pivotal role in ensuring the efficiency and adaptability of industrial systems. The adjustment mechanism of these bearings is engineered for precision and ease of use, allowing for straightforward modification of shaft tension. Often incorporating threaded rods or set screws, the mechanism facilitates simple and controlled adjustments, enabling maintenance personnel to fine-tune the tension according to the specific requirements of the application. Some take-up bearings feature self-aligning designs, providing additional flexibility in compensating for shaft misalignment during the adjustment process. This adaptability is crucial in maintaining optimal performance and prolonging the lifespan of conveyor or drive systems. The adjustment mechanisms exemplify the user-friendly and versatile nature of take-up bearings, contributing to their indispensability in the dynamic landscape of industrial machinery.
Advantages of Take-Up Bearings
Flexibility in Tension Adjustment: One of the primary advantages of take-up bearings is their ability to facilitate easy and precise tension adjustment in conveyor or drive systems. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing issues such as slack or excessive strain on components.
Accommodation of Thermal Expansion: Take-up bearings excel in absorbing and managing the axial movement of shafts caused by thermal expansion. This feature ensures that the system can operate effectively despite variations in temperature, contributing to overall stability and reliability.
Shaft Misalignment Compensation: These bearings provide support for shaft misalignment, helping to maintain proper alignment in industrial machinery. This capability reduces stress on the system, minimizes wear on components, and promotes longer equipment lifespan.
Reduced Maintenance Requirements: By enabling controlled movement and preventing unnecessary strain on components, take-up bearings contribute to the reduction of wear and tear. This, in turn, leads to lower maintenance requirements, saving time and resources in industrial settings.
Versatility in Mounting Configurations: Take-up bearings come in various types and housing styles, such as frame type, center pull, top angle, wide-slot, and side-mount. This versatility allows for the selection of the most suitable bearing based on specific mounting constraints or requirements, enhancing their applicability in diverse industrial applications.
Challenges and Solutions
Misalignment Issues: Take-up bearings may face misalignment problems due to changes in load or shaft movement. Select self-aligning take-up bearings that can compensate for misalignments, ensuring proper functioning even in dynamic conditions.
Wear and Fatigue: Continuous adjustments and dynamic conditions may lead to wear and fatigue in take-up bearings, affecting their lifespan. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and selecting bearings with durable materials and coatings can mitigate wear issues and enhance longevity.
Corrosion and Contamination: Exposure to harsh environments can result in corrosion and contamination, impacting the performance of take-up bearings. Choose bearings with corrosion-resistant materials, seals, and shields. Implement regular cleaning and maintenance practices to prevent contamination.
Over-Tension or Slack: Improper tension adjustment can lead to over-tension or slack in the system, affecting performance. Employ precision adjustment mechanisms and follow manufacturer guidelines for tension setting. Regularly monitor and adjust tension as needed.
Limited Space Constraints: Some applications may have limited space for take-up bearing installation. Utilize compact or specially designed take-up bearings, such as center pull or side-mount types, to accommodate space constraints while still providing effective tension adjustment.
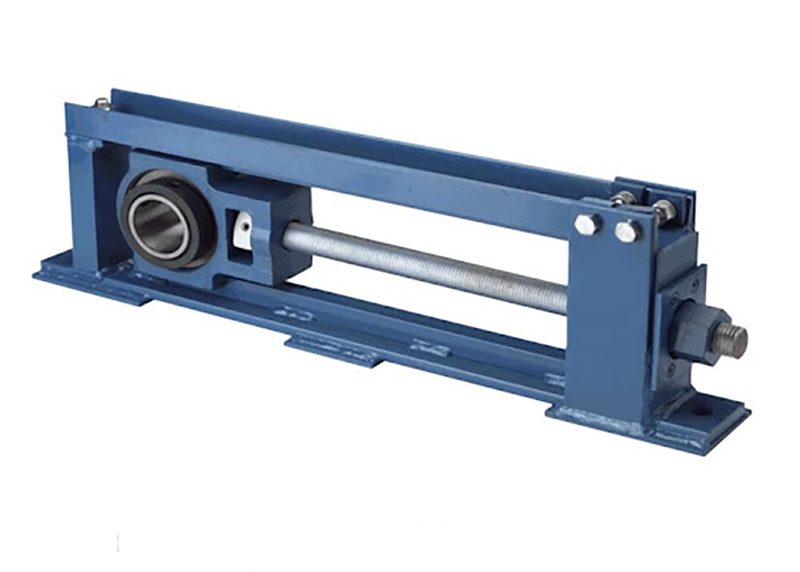

Common Applications
Conveyor Systems: Take-up bearings are widely used in conveyor systems to maintain proper tension in belts or chains. They accommodate dynamic conditions and thermal expansion, ensuring continuous and efficient material handling in industries like manufacturing, mining, and logistics.
Drive Systems: In various drive systems, such as those in industrial machinery and manufacturing equipment, take-up bearings are employed to absorb shaft movement, support misalignment, and enable easy tension adjustment, contributing to the smooth and reliable operation of the drive mechanisms.
Agricultural Equipment: Take-up bearings find application in agricultural machinery, particularly in equipment like combine harvesters and conveyors. They play a crucial role in maintaining proper tension in belts or chains, enhancing the efficiency and longevity of the equipment.
Material Handling Equipment: Take-up bearings are utilized in material handling equipment like elevators and lifts to manage shaft movements, accommodate thermal expansion, and enable precise tension adjustments. This ensures safe and efficient vertical transportation of goods and people.
Mining Machinery: In the mining industry, where heavy-duty equipment is prevalent, take-up bearings are employed in conveyors, crushers, and other machinery to support shaft movement, compensate for misalignment, and facilitate tension adjustments, contributing to reliable and durable operations in challenging environments.
Maintenance Practices
Regular Lubrication: Implement a routine lubrication schedule for take-up bearings. Proper lubrication helps reduce friction, minimizes wear, and ensures smooth operation. Use the recommended lubricants and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for intervals and quantities.
Periodic Inspection and Adjustment: Conduct regular inspections of take-up bearings to identify any signs of wear, misalignment, or damage. Adjust the tension as needed to maintain optimal performance. Address issues promptly to prevent further damage and extend the lifespan of the bearings.
Cleaning and Contamination Prevention: Keep the surrounding environment clean to prevent contamination of take-up bearings. Regularly clean the bearings and their housing to remove debris, dust, and other contaminants that could compromise performance. Use appropriate seals and shields to minimize exposure to harsh elements.
Replacement of Worn Components: Monitor the condition of take-up bearings during inspections and replace any worn or damaged components promptly. This may include bearings, seals, or other parts. Timely replacement helps prevent more extensive damage and ensures the continued reliability of the bearing system.
Selection Criteria
Selecting the appropriate take-up bearings is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of industrial machinery. The choice of bearings depends on various factors, including the specific application requirements, load conditions, and environmental factors. Considerations such as load capacity, shaft speed, and the degree of misalignment that the bearing must accommodate play a pivotal role in the selection process. Additionally, the operating environment, including temperature, moisture levels, and exposure to contaminants, influences the choice of materials and coatings. By carefully evaluating these factors and adhering to manufacturer recommendations, one can make informed decisions in selecting take-up bearings that align with the unique demands of the industrial application, promoting reliability and efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, take-up bearings are indispensable components in industrial machinery, offering crucial solutions for tension adjustment, misalignment support, and thermal expansion absorption. Their diverse types and housing styles showcase adaptability, providing versatility in meeting specific industrial needs. The advantages of easy adjustment, reduced maintenance, and versatility in mounting configurations highlight their significance. However, challenges like misalignment and wear necessitate proper maintenance practices. Selecting the right bearings based on load conditions and environmental factors is essential for optimal performance. In applications ranging from conveyor systems to mining machinery, take-up bearings play a pivotal role in ensuring reliable and efficient operation, contributing to the overall longevity of industrial equipment.
References
- 1.”Find The Best Take-Up Bearings Online” from Motion Industries;
- 2. “Take-Up Flange Unit Bearings” from Bearings Direct;
- 3. “Take-up ball bearing units” from SKF Bearings.


















