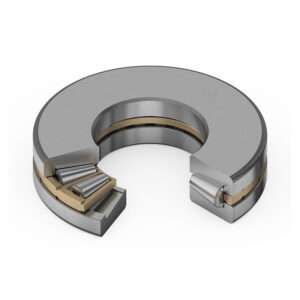
Tapered Roller Thrust Bearings
Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (28)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
Definition
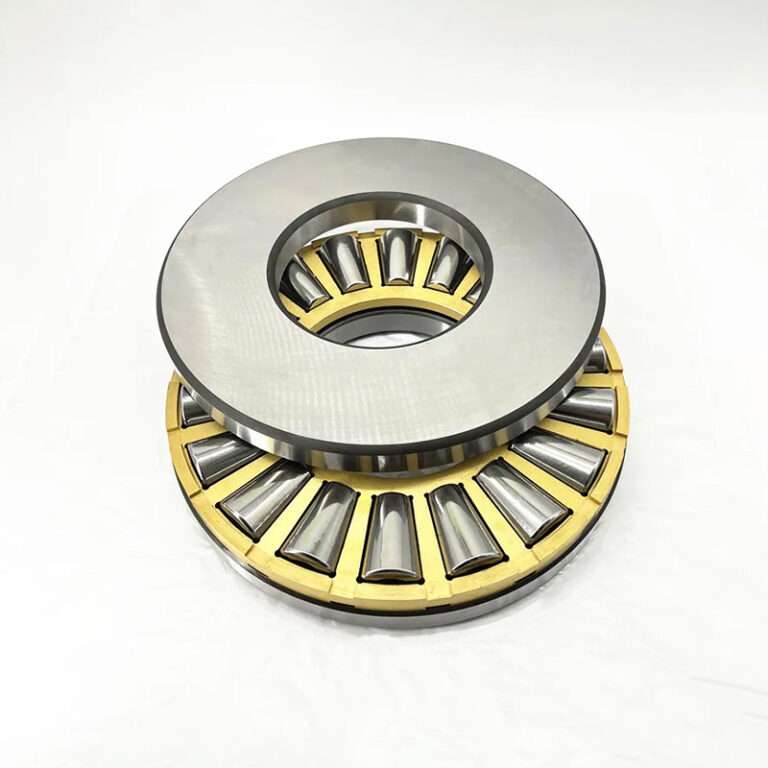
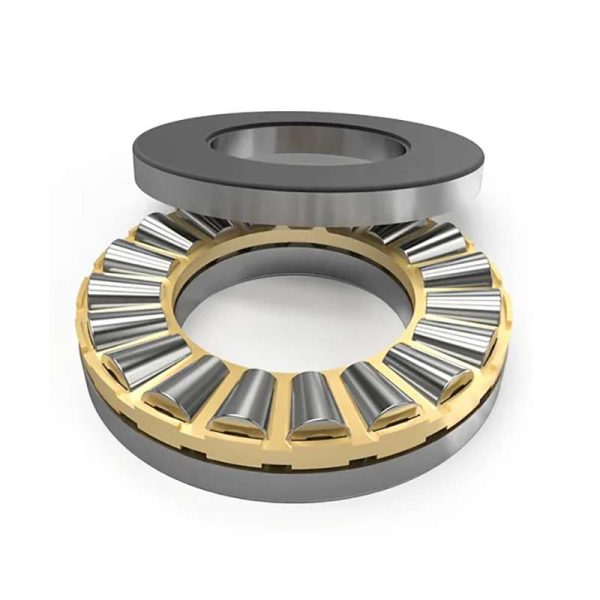
Tapered roller thrust bearings are precision-engineered components designed to handle axial loads by facilitating smooth, controlled rotation between two surfaces, ensuring optimal performance and durability in various applications.
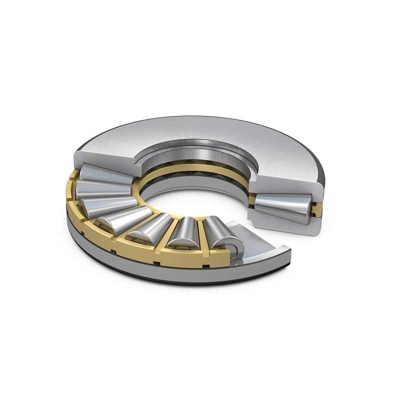

FHD Bearings is an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturing enterprise that stocks a full range of Cylindrical Roller Bearings,Tapered Roller Bearings,Spherical Roller Bearings,Needle Roller Bearings,Thrust Roller Bearings and Crossed Roller Bearings. With over 1,200 different bearing sizes and over 250K bearings in stock.
Materials
Rollers
- Chrome Steel: Provides high strength, hardness, and wear resistance for efficient load-bearing capabilities.
- Stainless Steel: Offers corrosion resistance, suitable for applications requiring resistance to rust and corrosion.
Cage
- Steel: Provides strength and rigidity to hold and separate the rollers, commonly used for its durability.
- Brass: Known for corrosion resistance, particularly in environments with moisture or aggressive conditions.

Washers
- Chrome Steel: Provides robust support and load distribution, ensuring durability under heavy axial loads.
- Alloy Steels: Used in some cases for enhanced specific properties such as increased toughness.
Features
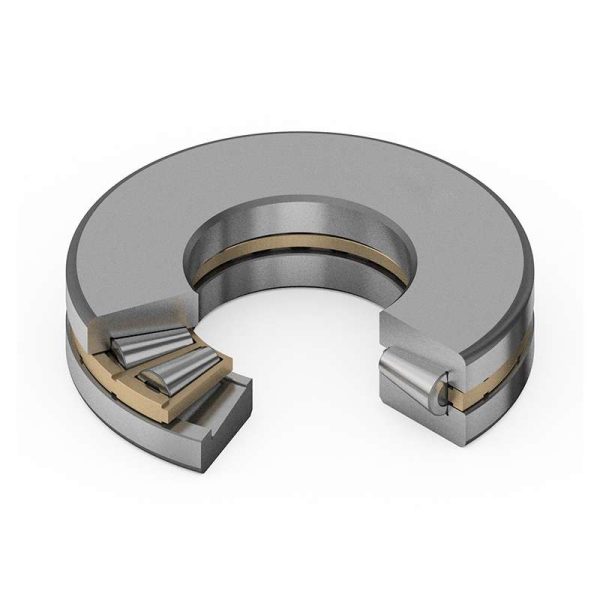

1.Tapered Rollers: Efficiently handle axial and radial loads, providing increased load capacity and precise load distribution.
2.High Load-Carrying Capacity: Offers superior capacity for heavy axial loads, making them ideal for demanding applications.
3.Reduced Friction: Maintains proper roller spacing, minimizing friction and wear for enhanced efficiency and longevity.
4.Precision Control: Ensures accurate axial movement control, crucial for applications requiring precision and control.
5.Combined Axial and Radial Support: Versatile bearings capable of supporting both axial and radial loads simultaneously.
6.Temperature Stability: Designed for stability across a range of temperatures, suitable for diverse operating conditions.
Advantages
1.High Load Capacity: Tapered roller thrust bearings excel at handling heavy axial loads due to their efficient load distribution along the tapered rollers.
2.Axial Rigidity: These bearings offer high axial rigidity, ensuring stable and precise shaft positioning under axial loads, making them suitable for applications where accurate positioning is critical.
3.Reduced Friction: The tapered design of the rollers minimizes friction during operation, leading to lower energy consumption and increased overall efficiency in applications where friction reduction is essential.
4.Space-Saving Design: Tapered roller thrust bearings have a compact design, allowing for efficient use of limited installation space. This makes them ideal for applications with spatial constraints.
5.High Speed Capability: Tapered roller thrust bearings can handle high speeds effectively, making them suitable for applications where rotational speed is a crucial factor.
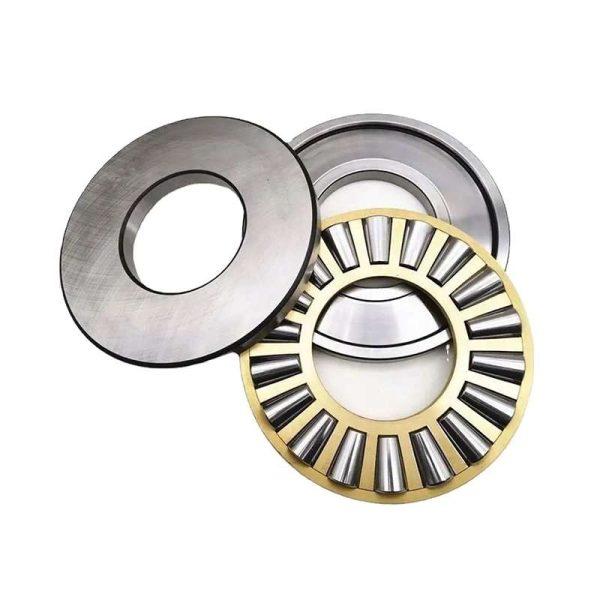
6.Ease of Assembly: These bearings are relatively easy to assemble, thanks to their separate components, including shaft washer, housing washer, and roller and cage assembly.
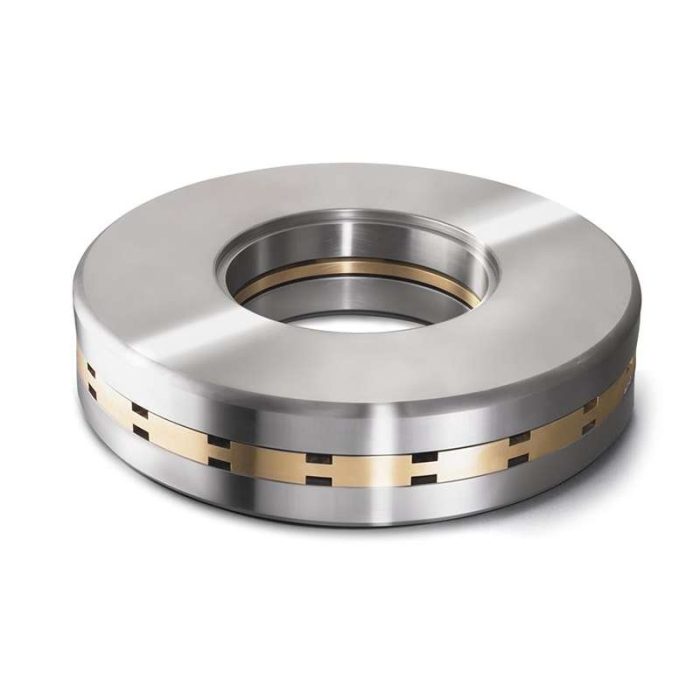

Applications
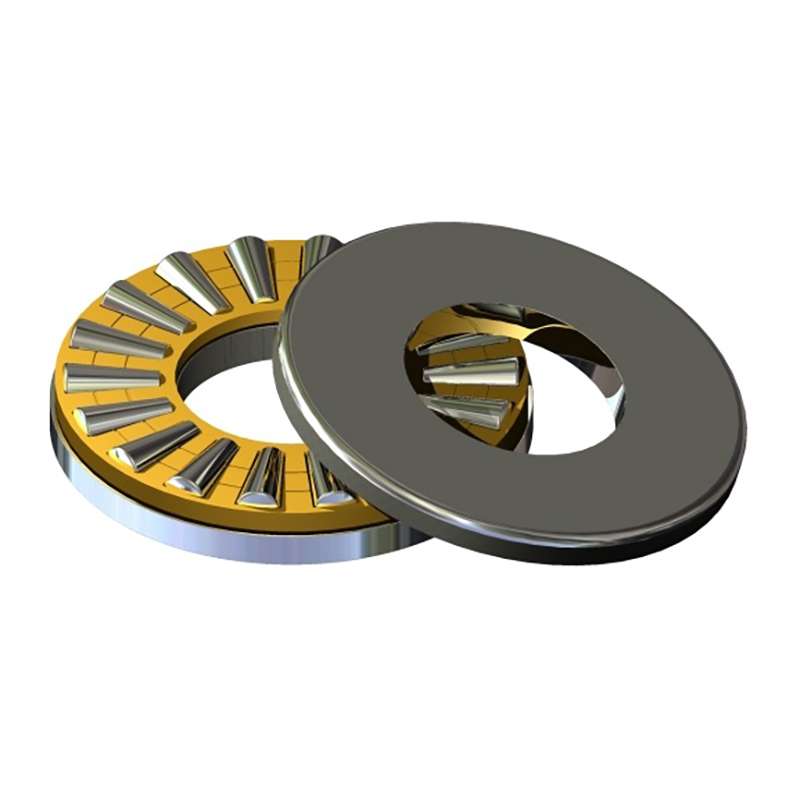

- Automotive Transmissions: Handling axial loads in transmissions.
- Mining Equipment: Supporting axial loads in crushers and conveyors.
- Aerospace Industry: Used in aircraft landing gear systems.
- Machine Tools: Supporting axial loads in precision machining.
- Marine Propulsion Systems: Managing axial loads in marine propulsion.
- Railway Axle Boxes: Ensuring smooth operation in train axle boxes.
- Steel Industry: Supporting axial forces in steel mills’ heavy machinery.
- Wind Turbines: Used in main shafts to handle axial loads.
Key Manufacturing Process of Tapered Roller Thrust Bearings
Forging and Heat Treatment: Shape raw materials through forging and apply heat treatment for desired hardness.
Turning and Grinding: Precision turning and grinding for accurate dimensions and smooth surfaces.
Roller and Cage Assembly: Assemble rollers into cages, ensuring proper spacing and alignment.
Case Carburizing: Enhance surface hardness and wear resistance through case carburizing.
Precision Machining: Hone and lap components for specified tolerances and surface finishes.
Quality Control and Inspection: Implement rigorous checks for dimensions, surface quality, hardness, and material properties to ensure quality standards are met.

FAQ - Frequently Asked Questions

A tapered roller thrust bearing is a type of rolling element bearing designed to handle axial loads, where the rollers are tapered in shape to distribute the load efficiently.
They are used in various applications such as automotive transmissions, mining equipment, aerospace, machine tools, marine propulsion, railway axle boxes, wind turbines, and steel industry machinery.
Tapered roller thrust bearings have a unique tapered design that allows for efficient axial load handling, reduced friction, and high-speed capability.
The tapered design of the rollers enables them to support axial loads by distributing the force along the length of the rollers, providing stability and rigidity.
The tapered design reduces friction, enhances load distribution, and allows for a higher load capacity in a more compact space compared to some other thrust bearings.
Precision machining, including turning, grinding, honing, and lapping, ensures accurate dimensions, smooth surfaces, and tight tolerances, contributing to the bearings’ reliability and performance.
They are assembled by combining separate components, including shaft washers, housing washers, and roller and cage assemblies, making installation relatively straightforward.
Case carburizing enhances the surface hardness and wear resistance of the bearing components, ensuring durability and longevity in demanding operational conditions.
The reduced friction in tapered roller thrust bearings leads to lower energy consumption, making them more energy-efficient in various applications.
Quality control involves dimensional checks, surface quality assessments, and testing for hardness and material properties to ensure that each bearing component meets stringent quality standards.
Installation and Maintenance
Installation
- Clean and Inspect: Ensure cleanliness and inspect components for damage.
- Apply Lubrication: Lubricate all parts with suitable lubricant for the operating conditions.
- Assemble Components: Carefully assemble components following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Adjust Clearance or Preload: Set clearance or preload per manufacturer specifications for proper load distribution.
- Mount onto Shaft: Slide the assembled bearing onto the shaft, ensuring proper seating and alignment.
- Secure and Lock: Secure the housing washer, and apply axial locking mechanisms as instructed to prevent axial movement.


Maintenance
- Regular Lubrication: Follow recommended intervals for proper lubrication using the specified lubricant.
- Monitoring and Inspection: Conduct routine inspections to detect signs of wear, damage, or misalignment.
- Proper Storage: Store bearings in a clean, dry environment as per manufacturer recommendations.
- Temperature Control: Maintain operating temperatures within the specified range to prevent premature wear.
- Handling during Installation and Removal: Exercise care to avoid shocks or impacts that could damage components.
- Alignment and Preload Adjustment: Ensure proper alignment during installation and periodically check and adjust preload as needed.