Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (28)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
Enhancing Durability: Ball Transfer Unit Care Strategies
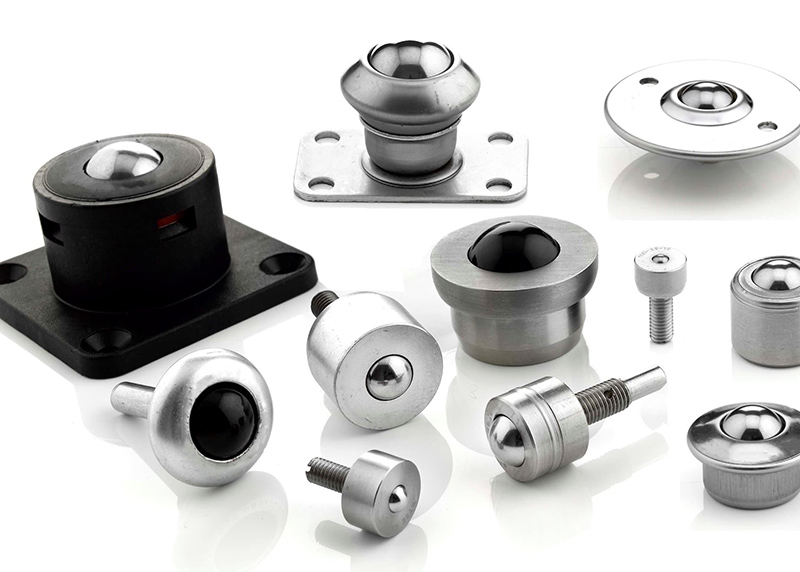

Introduction
Proper installation, maintenance, and lubrication are crucial for maximizing the service life of ball transfer units, which play a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient material handling. These components are essential in various applications, including conveyor systems, cargo handling, and assembly lines, where they enable the easy movement of heavy loads. Ensuring these units are correctly installed, regularly maintained, and adequately lubricated helps prevent premature wear, reduces downtime, and maintains optimal performance, ultimately leading to increased efficiency and cost savings in industrial operations.
Understanding Ball Transfer Units
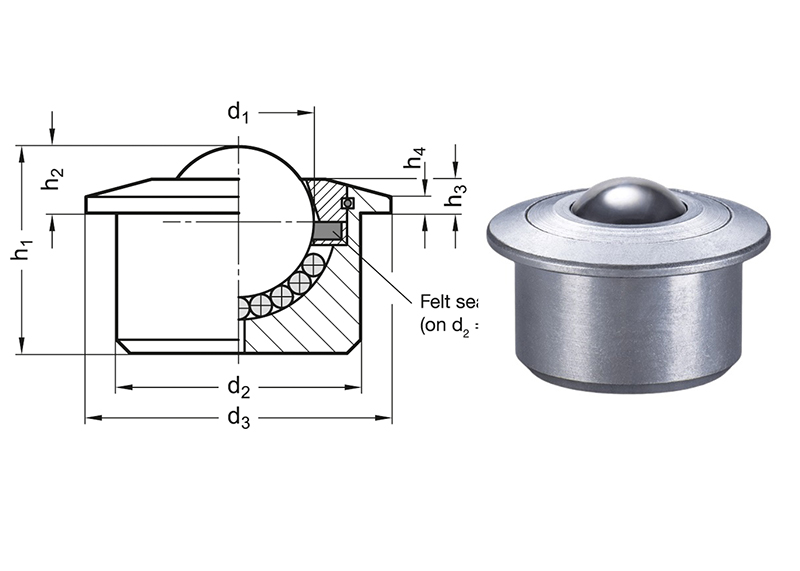
Ball transfer units are omnidirectional load-bearing devices that facilitate the smooth and easy movement of objects in any direction. Comprised of a large load-bearing ball seated within multiple smaller support balls encased in a housing, these units function by reducing friction, allowing heavy loads to glide effortlessly across surfaces.
They are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and aerospace, where they serve critical roles in conveyor systems, cargo handling, and assembly lines. In manufacturing, they streamline the transfer of heavy components between workstations. In logistics, they enhance the efficiency of packaging and sorting operations. Aerospace applications utilize them for the precise handling of delicate components.
The construction of ball transfer units typically includes a durable steel or stainless steel housing, ensuring robustness and longevity. The primary load-bearing ball, often made of hardened steel or other materials depending on the application, sits atop smaller support balls, which help distribute the load evenly and reduce friction. Understanding these components and their construction is key to selecting the right ball transfer units for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Proper Installation Practices
Pre-installation inspection and preparation
Proper installation practices for ball transfer units begin with thorough pre-installation inspection and preparation. This step is crucial to ensure the units perform optimally and have a long service life. Inspect the units for any defects or damage that might have occurred during shipping or handling. Check for proper alignment and ensure all components are intact. Surface preparation is also essential; the mounting surface must be clean, level, and free from debris to prevent misalignment and uneven wear. Securing the units properly using recommended attachment methods, such as bolts or welds, ensures they remain stable under operational loads. Careful pre-installation preparation helps avoid potential issues and contributes to the smooth operation of ball transfer units.
Mounting guidelines
Alignment and adjustment techniques
Proper alignment and adjustment techniques are integral to the successful installation of ball transfer units, ensuring their optimal performance and longevity. After mounting, it’s crucial to align the units correctly to prevent issues such as uneven wear or jerky movement. This involves ensuring that the units are positioned parallel to each other and aligned with the direction of movement. Any misalignment should be promptly corrected using adjustment techniques such as shimming or repositioning. Additionally, adjusting the height of the units to match the surrounding surface level helps maintain smooth operation and prevents strain on the components. By meticulously aligning and adjusting the ball transfer units during installation, potential issues can be mitigated, ensuring trouble-free operation and maximizing their service life.
Maintenance Guidelines
Regular inspection routines
Regular inspection routines are fundamental to maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of ball transfer units. Establishing a schedule for routine inspections ensures that any potential issues are identified early, preventing costly downtime and repairs. These inspections should encompass a thorough examination of key components such as ball bearings, seals, and housing for signs of wear, damage, or contamination. The frequency of inspections will depend on factors such as the operating environment and the intensity of use. By conducting regular inspections, maintenance personnel can detect and address issues promptly, extending the service life of the ball transfer units and optimizing their performance in material handling applications.
Cleaning procedures
Effective cleaning procedures are essential for maintaining the optimal functionality and longevity of ball transfer units. Regular cleaning helps remove debris, contaminants, and build-up that can impair the smooth operation of the units and accelerate wear and tear. It is crucial to use appropriate cleaning agents and methods to ensure thorough cleaning without causing damage to the components. Cleaning procedures should include removing dirt, dust, and any other foreign particles from the surface of the units and inspecting for signs of corrosion or damage. Implementing a consistent cleaning regimen as part of the maintenance routine helps prevent performance issues and extends the service life of ball transfer units, ensuring they continue to operate efficiently in various material handling applications.
Wear and tear assessment
Assessing wear and tear is a critical aspect of maintenance for ball transfer units to ensure their continued functionality and longevity. Regular evaluation of the units’ condition helps identify signs of wear, damage, or deterioration that could affect performance or lead to failure. Maintenance personnel should inspect key components such as ball bearings, housing, and seals for indications of excessive wear, such as visible damage, uneven surfaces, or loss of lubrication. Establishing clear criteria for determining when components need replacement based on wear assessment findings ensures proactive maintenance and minimizes the risk of unexpected failures. By conducting thorough wear and tear assessments as part of the maintenance routine, organizations can optimize the performance and service life of ball transfer units, contributing to smooth material handling operations across various applications.
Lubrication Techniques
Lubrication techniques are fundamental to the maintenance and optimal performance of ball transfer units, significantly contributing to their longevity and efficiency. Proper lubrication reduces friction between moving parts, minimizing wear and tear while preventing corrosion and other forms of damage.
The choice of lubricant, whether grease or oil, depends on the specific application and operating conditions, with each type offering distinct advantages in terms of load capacity, temperature tolerance, and contamination resistance. Lubrication schedules must be carefully established, taking into account factors such as operational load, speed, and environmental conditions to determine the appropriate frequency and quantity of lubrication.
Applying the lubricant correctly is crucial; it should be distributed evenly to reach all necessary components, ensuring comprehensive coverage and effectiveness. Additionally, monitoring the condition of the lubricant, such as checking for contamination or degradation, helps maintain optimal lubrication levels and performance.
By implementing proper lubrication techniques, organizations can significantly extend the service life of ball transfer units, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance the reliability of material handling systems in various industrial applications.
Best Practices for Lubrication
Proper lubrication application methods
Proper lubrication application methods are essential for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of ball transfer units. Ensuring the right quantity and even distribution of lubricant is crucial to reducing friction and wear. When applying lubrication, it is important to follow manufacturer guidelines, which specify the type and amount of lubricant suitable for the units. Techniques such as using a grease gun for precise application or manually spreading lubricant to reach all components ensure comprehensive coverage. Additionally, paying attention to hard-to-reach areas and applying lubricant to these spots helps maintain optimal performance. By adhering to proper lubrication application methods, the service life of ball transfer units can be significantly extended, ensuring reliable operation in various material handling applications.
Monitoring lubricant effectiveness
Monitoring lubricant effectiveness is vital for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of ball transfer units. Regularly checking the condition of the lubricant helps detect signs of contamination, degradation, or insufficient lubrication. Visual inspections and tools such as oil analysis can be used to assess the lubricant’s quality and performance. Indicators of inadequate lubrication include increased friction, unusual noises, or visible wear on components. By consistently monitoring lubricant effectiveness, maintenance personnel can identify issues early and take corrective actions, such as replenishing or replacing the lubricant. This proactive approach helps maintain the smooth operation of ball transfer units, reducing downtime and extending their service life.
Compatibility considerations
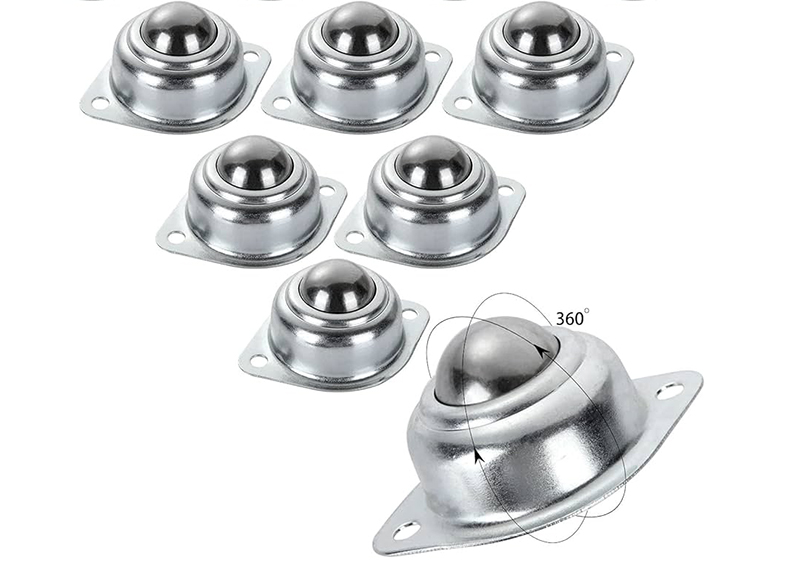

Operating Conditions and Service Life
The operating environment significantly impacts the service life and performance of ball transfer units. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, and exposure to contaminants can affect the units’ functionality and durability. High temperatures can degrade lubricants and materials, while low temperatures may cause brittleness. Humidity and moisture can lead to corrosion and rust, compromising the units’ integrity.
Load and speed considerations are also critical; exceeding the recommended load capacity can result in excessive wear, deformation, or failure of the units. Similarly, high operating speeds can increase friction and heat, accelerating wear and reducing the lifespan of the ball transfer units. Environmental factors, including dust, dirt, and chemical exposure, can further exacerbate wear and contamination, leading to operational issues.
Properly evaluating and addressing these conditions by selecting appropriate materials, lubricants, and protective measures is essential for maintaining the performance and extending the service life of ball transfer units. By understanding and mitigating the impact of these operating conditions, industries can ensure reliable and efficient material handling operations, maximizing the longevity and effectiveness of their ball transfer units.
Conclusion
Proper installation, maintenance, and lubrication are vital for maximizing the service life and performance of ball transfer units in various industrial applications. These units, essential in conveyor systems and cargo handling, facilitate the smooth movement of heavy loads. Effective installation involves thorough inspection, alignment, and secure mounting. Regular maintenance, including inspections, cleaning, and wear assessments, ensures ongoing functionality. Lubrication reduces friction and prevents corrosion, extending unit longevity. Understanding and mitigating the impact of operating conditions, such as temperature and load, further enhance durability. By following these best practices, industries can ensure efficient material handling, reduced downtime, and cost savings.
References
- 1.”Ball Transfer Units” from Wikipedia;
- 2. “Ball Transfer Units” from Bridge Bearings;
- 3. “Fitting tips and technical data for Ball Transfer Units” from KIPP.


















