Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (28)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
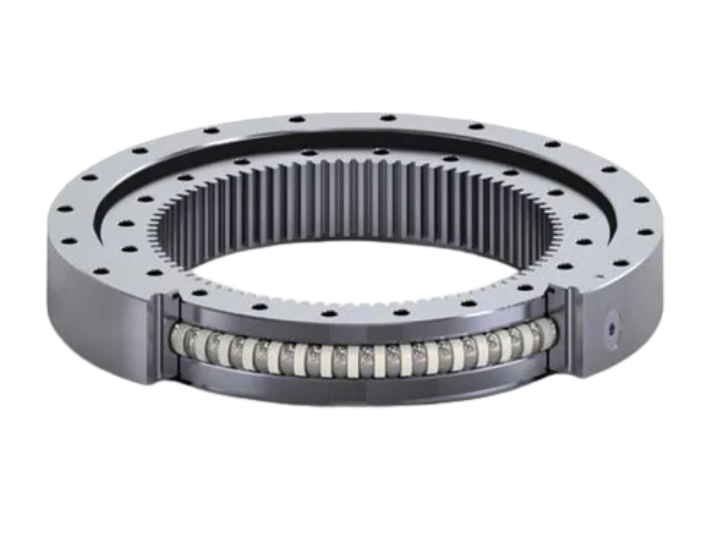
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
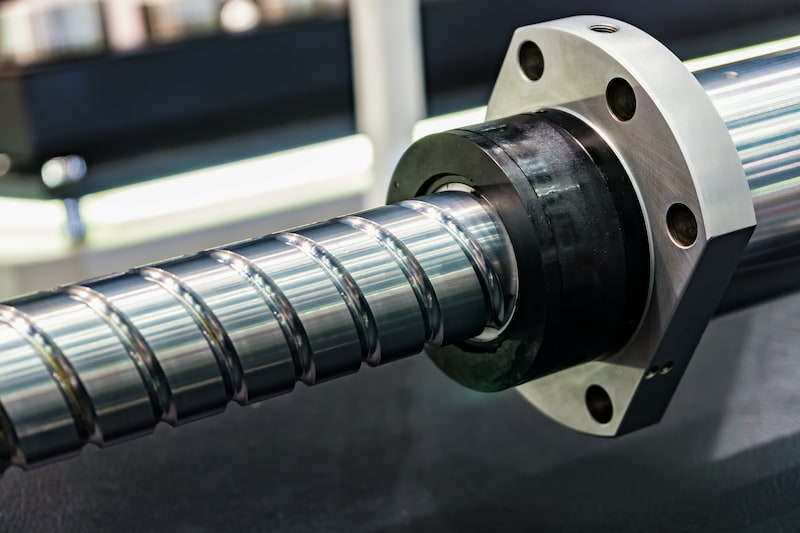
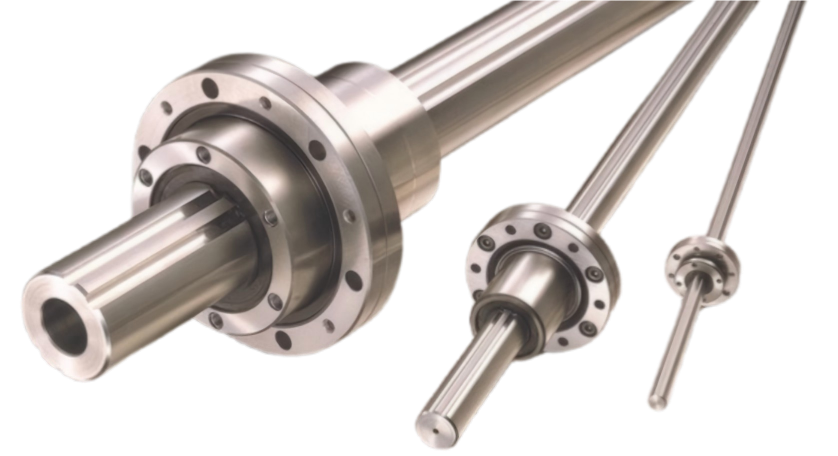
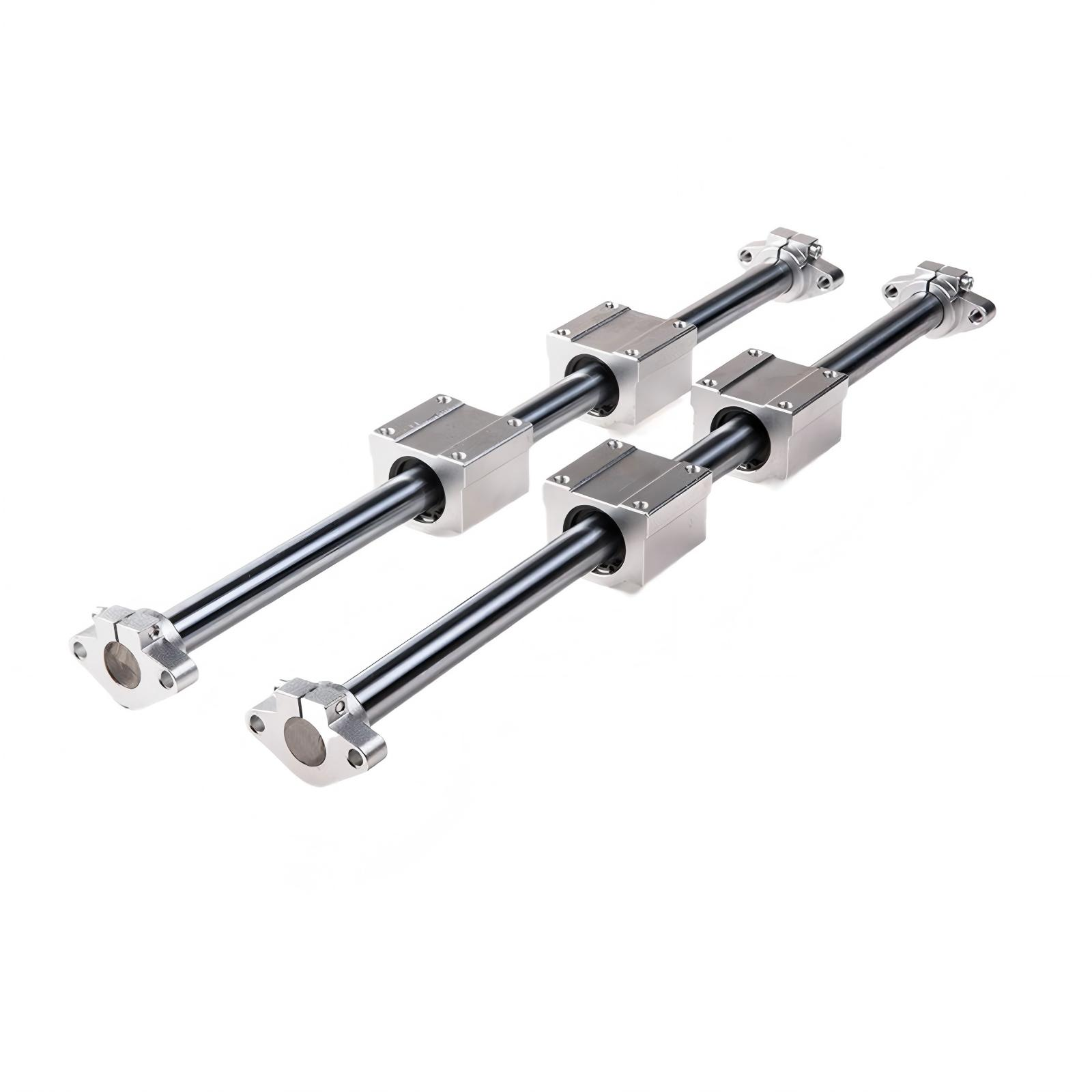
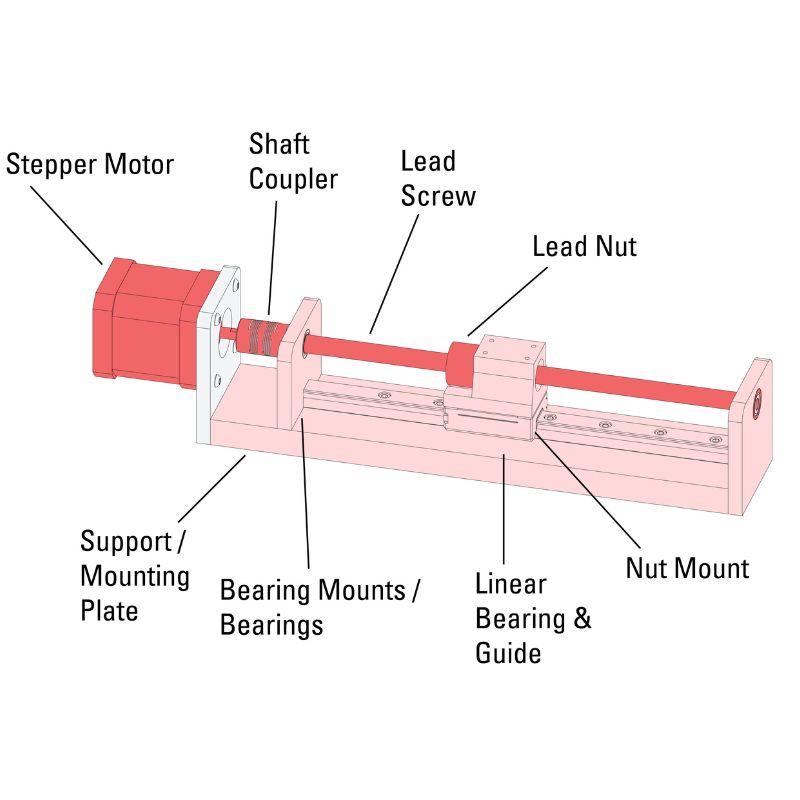
Lead Screw Bearings:How Much Do You Know
Introduction
Lead screws are a critical component of many machine tools, such as lathes, mills, and grinders. They are used to convert rotary motion into linear motion, and they are essential for providing smooth, accurate movement.
Lead screw bearings support the lead screw and help to reduce friction. There are a variety of different types of lead screw bearings, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
In this blog post, we will take a detailed look at lead screw bearings.We will discuss the different types of bearings, and the factors to consider when choosing a lead screw bearing.
Types Of Lead Screw Bearings
There are four main types of lead screw bearings:
- Ball bearings are the most common type of lead screw bearing. They are made of two sets of balls and races, which are held together by a cage. Ball bearings provide good performance in terms of load capacity, speed, and accuracy.
- Roller bearings are another type of lead screw bearing. They are made of a series of rollers that are arranged in a cylindrical or conical shape. Roller bearings provide good performance in terms of load capacity and speed, but they are not as accurate as ball bearings.
- Sleeve bearings are a third type of lead screw bearing. They are made of a single piece of metal that is shaped to fit around the lead screw. Sleeve bearings provide good performance in terms of load capacity and speed, but they are not as accurate as ball or roller bearings.
- Hydrostatic bearings are a fourth type of lead screw bearing. They are made of a series of small fluid chambers that are arranged around the lead screw. Hydrostatic bearings provide very high levels of accuracy, but they are also the most expensive type of lead screw bearing.
The type of lead screw bearing that is best for a particular application will depend on the specific requirements of the application. For example, if accuracy is a critical factor, then a hydrostatic bearing would be a good choice. If load capacity and speed are more important, then a ball or roller bearing would be a better choice.
In addition to the four main types of lead screw bearings, there are also a number of other types of bearings that can be used in lead screw applications. These include:
- Thrust bearings are designed to support axial loads. They are typically made of a single piece of metal that is shaped to fit around the lead screw.
- Anti-friction bearings are designed to reduce friction between the lead screw and the nut. They are typically made of a soft material, such as nylon or Teflon.
- Composite bearings are made of a combination of materials, such as metal and plastic. They offer the best of both worlds in terms of load capacity, speed, and accuracy.
The type of bearing that is best for a particular lead screw application will depend on the specific requirements of the application. For example, if the lead screw is subject to high axial loads, then a thrust bearing would be a good choice. If the lead screw is operating at high speeds, then an anti-friction bearing would be a good choice. If accuracy is a critical factor, then a composite bearing would be a good choice.
How To Choose The Right Lead Screw Bearings
Lead screw bearings are used to support the lead screw in a lead screw linear motion system. The lead screw is the threaded shaft that converts rotary motion into linear motion. The bearing must be able to support the load of the lead screw and the applied forces, while also providing smooth, low-friction motion.
There are a number of factors to consider when choosing a lead screw bearing, including:
- Load capacity: The bearing must be able to support the weight of the lead screw and the applied forces. The load capacity is typically expressed in pounds per inch (lb/in) or kilograms per millimeter (kg/mm).
- Speed: The bearing must be able to operate at the desired speed without overheating or seizing. The speed rating is typically expressed in revolutions per minute (rpm).
- Torque: The bearing must be able to withstand the torque applied to the lead screw. The torque rating is typically expressed in inch-pounds (in-lb) or Newton-meters (N-m).
- Temperature range: The bearing must be able to operate within the desired temperature range. The temperature range is typically expressed in degrees Fahrenheit (°F) or degrees Celsius (°C).
- Contamination: The bearing must be able to operate in a clean environment or be protected from contaminants.
- Cost: The bearing must be within the desired budget.

Regular Maintenance For Optimal Performance
Regular Lubrication
Good lubrication is essential for lead screw bearings to maintain efficient operation. Regular application of appropriate lubricants ensures that the bearing surfaces are adequately lubricated to minimize friction and wear. Choose a lubricant that is suitable for the working environment, such as special lubricants for high temperature or high pressure conditions, to ensure that the bearings maintain optimal performance under various working conditions.
Periodic Inspection and Cleaning
Establish a regular inspection and cleaning program to ensure that lead screw bearings are in optimum condition. Remove dust, dirt and foreign matter that may accumulate around the bearings to prevent them from damaging the bearing surfaces.
Environmental Monitoring and Control
Lead screw bearings operate in a variety of operating environments and environmental conditions can have a significant impact on their performance. Environmental monitoring and control is implemented to ensure that the bearings are operated under the right conditions of temperature, humidity and cleanliness.
Monitoring of vibration and noise
Monitor the operating conditions of lead screw bearings in real time by using vibration and noise monitoring equipment. Abnormal vibration or noise can be an indicator of potential problems. Establishing a regular monitoring program avoids production interruptions due to bearing failures by identifying problems early and taking corrective action.
Tighten bolts and fittings regularly
Looseness of the bearing bracket and adjacent components may result in erratic operation and damage to the leadscrew bearing. Regularly check the tightening bolts and fittings to ensure that they are in the correct tightening condition.
Record and analyze data
Establish a maintenance record system to keep detailed records of each maintenance activity and bearing operating data. Use this data for trend analysis to predict potential problems and develop more effective maintenance strategies.
Conclusion
Lead screw bearings are a critical component of many machine tools. They are used to convert rotary motion into linear motion, and they are essential for providing smooth, accurate movement.
There are a variety of different types of lead screw bearings, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The best type of bearing for a particular application will depend on the load, speed, accuracy, and environmental conditions.
References
- 1.Something about ”lead screw“ from Wikipedia;
- 2.More information about “lead screw bearings” from IGUS ;
- 3.Some information about “lead screw bearings” from Iqsdirectory.



















