Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (27)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
Insulated Bearings: Enhancing Motor Performance And Reliability
In modern industrial development and high-efficiency motor design, insulated bearings not only enhance the performance of motors, but also significantly increase their reliability. Insulated bearings protect the integrity of the bearing and the motor by preventing galvanic corrosion and other electrical damage through their unique design, which effectively shields the motor from harmful currents that may be generated during operation. This article will delve into the basic concepts, types, and advantages of using insulated bearings and analyze why it is important to use them in electric motors.
Insulated bearings are bearings that can block the passage of electric current and have insulating properties of the bearing itself. Its insulating properties are usually ensured by using a special process to cover a layer of insulating material on the outer or inner ring of the bearing, or by using ceramics for its rolling body.
Its main function is to prevent current from passing through the bearing, thus effectively protecting the motor from damage caused by stray current or electric arc.


- Introduction of insulating materials
Electrically insulated bearings introduce insulating materials, such as ceramic or plastic composites, which are used to isolate the conductive elements inside and outside the bearing. This insulating material effectively prevents the conduction of current and solves the conductivity problem. - Isolation design of inner and outer rings
Electrically insulated bearings are designed to ensure good isolation between the inner and outer rings to prevent current conduction inside the bearing. This isolation design is a key step in realizing electrical insulation. - Use of insulating lubricants
The selection of a lubricant with good insulating properties is another important principle for electrically insulated bearings. A good insulating lubricant reduces the risk of electrical failure and ensures proper lubrication of the bearing. - Optimization of heat dissipation
To ensure the stable operation of electrical insulated bearings under high load and high speed, the design also considers the optimization of heat dissipation performance. Through a good heat dissipation structure and an efficient lubrication system, the bearings can effectively dissipate the heat generated and prevent overheating.
Insulated bearings, as a device specifically designed to prevent damage caused by the passage of electric current through the bearing, come in two main types: coated insulated bearings and ceramic insulated bearings.
1. Coated insulated bearings
- Coated insulated bearings achieve their insulating effect by applying an insulating coating to the outer surface or internal components of the bearing. This coating is usually made of a high-resistance material, such as epoxy resin or polyimide, which effectively blocks the passage of electric current. Bearings made of this material are usually less costly.
2. Ceramic Insulated Bearings
- Ceramic insulated bearings use ceramic materials (such as alumina or silicon nitride) instead of conventional metal rolling elements or bearing rings. Since ceramics are inherently non-conductive, this type of bearing provides a higher level of insulation. Bearings made of this material offer higher wear and corrosion resistance.
- Mitigation of electrical damage to motor components
Insulated bearings mitigate the effects of electrical damage to motor components by effectively blocking the path of current conduction within the bearing. By preventing the current from flowing to the sensitive bearing parts, the insulated bearing reduces the risk of damage to the motor in the event of electrical interference or accidental current flow and protects the long-term stable operation of the motor system.
- Preventing current-induced bearing failures
Conventional bearings are prone to bearing failure when disturbed by external currents. The use of insulated bearings can effectively prevent this from happening because the design of the insulated bearings can block the flow of current to the bearings and protect them from the influence of external currents, thus reducing the risk of current-induced bearing failure.
- Extended service life and reduced maintenance costs
Insulated bearings extend the overall service life of the motor system because they mitigate electrical damage to motor components and prevent bearing failure. By reducing the number of repairs and the amount of maintenance work, the use of insulated bearings also reduces maintenance costs and improves the reliability and operational efficiency of the equipment.
Why Insulated Bearing Used In Motor
The primary function of insulated bearings is to prevent current from passing through the bearing assembly. High-frequency currents or voltages caused by devices such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) may be present in or around motors, and these may flow through conventional metal bearings to motor components, causing motor failure or damage. The use of insulated bearings effectively isolates these current conduction paths and protects sensitive parts inside the motor from electrical damage, thus improving the stability and reliability of the motor.
Conventional metal bearings are susceptible to failure due to external current flow, resulting in shortened motor life. Insulated bearings reduce the risk of electrical damage and extend the life of the motor.
Motors often undertake critical production tasks in industrial production, and their downtime may lead to production interruptions and losses. Therefore, the use of insulated bearings can reduce the risk of motor failure due to electrical problems, and reduce the possibility of unplanned downtime, to protect the continuity and stability of production.
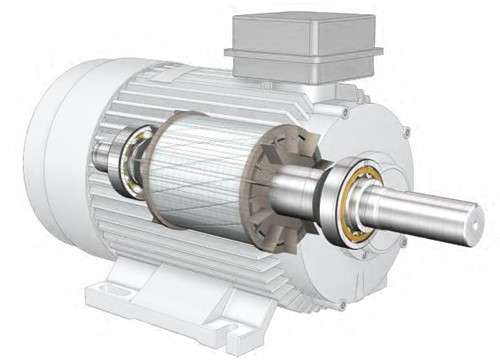
Insulated Bearings Should Be Used In What Circumstances
In high voltage or high current motors and generators, insulated bearings can prevent current from passing through the bearings due to induced voltage on the motor shaft, effectively preventing galvanic corrosion damage.
In motor systems using frequency converters, frequency conversion operation often introduces additional voltage and current problems that can lead to increased shaft currents, which can be avoided by using insulated bearings.
Since motors in electric vehicles typically operate at high voltages, insulated bearings can be used to prevent current from passing through the bearings, extending the life of the motor.
How Can Insulated Bearings Get Electrical Damage?
Although insulated bearings are designed to prevent electrical damage, they can still be subject to electrical damage under certain circumstances. This is mainly due to the fact that if the insulation fails or is damaged, induced voltages on the motor shaft may cause a current to flow through the bearing, triggering the so-called shaft current problem. When the shaft current passes through the bearing, it can generate tiny sparks between the rolling elements inside the bearing and the raceway. These sparks cause a phenomenon known as galvanic corrosion, which results in pitting or craters on the bearing surface, and this damage accelerates the wear of the bearing and reduces its service life.
To prevent electrical damage to insulated bearings, it is first necessary to ensure that the insulating layer of the bearing is not damaged during mounting and use. During installation, excessive force or improper tools should be avoided to avoid damaging the insulation layer.
Secondly, the insulation performance of the insulated bearings should be checked regularly to ensure that they maintain good insulation throughout their life cycle. In addition, measures such as grounding and insulating isolation products can be used to reduce the shaft voltage further, thereby reducing the electrical stress on the insulating bearings.
Excessive humidity and corrosive chemicals should also be avoided as much as possible in the environment where the motor is used, as these factors may affect the insulation effect of the insulating bearings.
What Are The Difference Between Insulated Bearings And Conventional Bearings?
Insulated Bearings
Insulated bearings are a kind of bearings coated with an insulating layer on the outer or inner ring of the bearings, the main function of which is to prevent the current from being conducted through the bearings, thus avoiding galvanic corrosion. They are commonly used in motors with variable frequency drives and in motors for electric vehicles.
Conventional Bearings
Conventional bearings are usually made of metal, such as steel or copper alloys, and do not have a special non-conductive protective layer; their main function is to support rotating or sliding parts and to reduce friction and wear during movement. They do not have the function of preventing current conduction. Widely used in a variety of machinery and equipment
Key Characteristics Of Electrically Insulated Bearings
1. Selection of insulating materials
One of the primary characteristics of electrically insulated bearings is the insulating material used. Common insulating materials include:
- Ceramics
Excellent insulating properties.
Resistant to high temperature and corrosion, suitable for harsh environments. - Plastic composites
Lightweight with good insulating properties.
Resistant to chemical corrosion and suitable for a wide range of industrial environments.
2. Design of insulation mechanisms
The design of electrically insulated bearings is concerned with effectively preventing the conduction of current through the bearing, where key design features include:
- Isolation design of inner and outer rings
The design ensures effective isolation between the inner and outer rings to prevent current conduction. - Selection of insulating lubricant
The use of a lubricant with good insulating properties ensures proper lubrication of the bearing while reducing the risk of electrical failure.
3. Optimization of heat dissipation
Under the working condition of high load and high speed, the heat dissipation performance is the key characteristic to ensure the stable operation of electrical insulation bearings:
- Heat dissipation structure design
Optimize the heat dissipation structure of the bearings to improve the heat dissipation efficiency and prevent overheating and performance degradation. - High efficiency lubrication system
The use of high-efficiency lubrication system reduces the heat generated by friction and maintains the bearings within the appropriate temperature range.
4. Reliable sealing system
- Ensure that the electrical insulation bearings are equipped with a reliable sealing system to prevent the intrusion of external substances such as dust and moisture, and to protect the performance of the insulating material from being impaired.
5. Durability and maintainability
- Focus on the durability of electrical insulation bearings to extend their service life.
At the same time, maintainability is taken into account to ensure easier and more economical maintenance of the bearings.
Application Areas Of Insulated Bearings
Insulated bearings are widely used in a variety of industrial and transportation applications because of their unique anti-electrical properties, including:
1. Electric motors and generators
2. Frequency converter driven equipment
3. Railroad traction motors
4. Electric vehicles
5. Wind power generation
6. Oil and gas industry
7. Heavy-duty applications and processing equipment
References
1. NSK Advantages of ”Insulated Bearings“
2. SKF detailed explanation of electrically ”insulated bearings“






















