Track Rollers
Table of Contents
Definition of Track Rollers
A track roller is a type of rolling bearing designed for use in track-type or linear motion applications. It consists of a cylindrical or needle roller, or a ball bearing, enclosed within a thick outer ring. Track rollers are used to support and guide heavy loads while allowing them to move along a defined path, commonly found in applications like conveyor systems, cam followers, and linear motion guides.

FHD Bearings is an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturing enterprise that stocks a full range of tracl rollers,thin section bearings,deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, thrust ball bearings, Self-aligning ball bearings and ceramic ball bearings. With over 1,200 different bearing sizes and over 250K bearings in stock.
Materials of Track Rollers
– Chrome-plated steel provides additional surface hardness and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for demanding environments.
– Stainless steel is chosen for its exceptional corrosion resistance. Bearings made from stainless steel are ideal for applications where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or corrosive environments is a concern.
– Some track rollers are made from high-strength plastic materials, which can reduce noise and offer corrosion resistance. They are often used in lighter-duty applications.
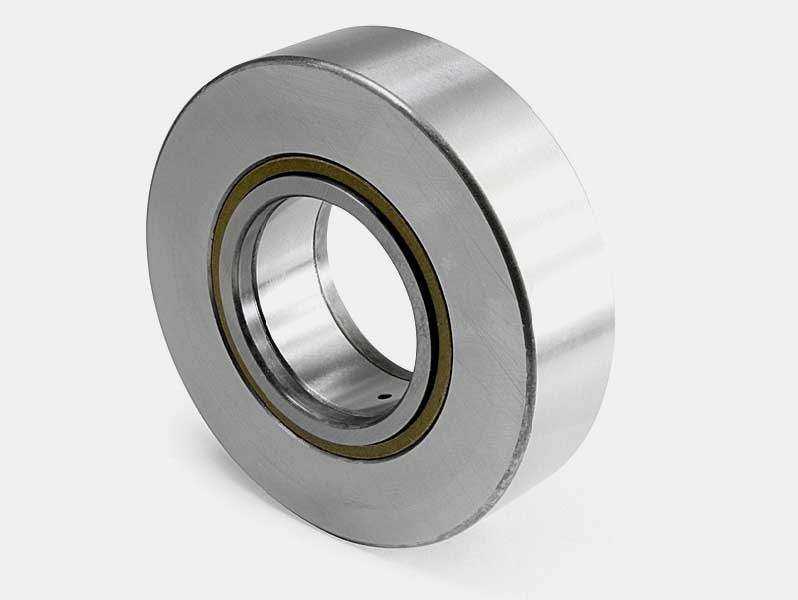

Ceramic
– Ceramic track rollers are known for their exceptional wear resistance, low friction, and high-temperature capabilities. They are commonly used in specialized applications.
Features of Track Rollers

- Outer Ring with a Cam Profile: Track rollers have an outer ring with a specialized cam profile that enables them to follow tracks or cam tracks.
- Stud or Shaft Mounting: They are typically mounted on a stud or shaft, which allows them to move along a defined path or track.
- Thick Outer Ring: Track rollers often have a thicker outer ring to provide robust support and load-bearing capacity.
- Full Complement of Rolling Elements: Some track rollers feature a full complement of rolling elements (balls or rollers), ensuring high load-carrying capacity.
- Built for Linear Motion: Track rollers are designed for linear motion applications, where they follow a path or track, rather than rotational motion like traditional bearings.
- Various Profile Options: They come in different profile shapes (e.g., cylindrical, V-groove, or crowned) to suit specific track configurations and load distribution requirements.
Advantages of Track Rollers
- High Load-Carrying Capacity: Track rollers are designed to handle significant radial and axial loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Precise Linear Motion: They offer precise and consistent linear motion along tracks or cam profiles, ensuring accurate positioning and movement.
- Reduced Friction and Wear: Track rollers are engineered to minimize friction, resulting in lower wear and longer service life.
- Minimal Maintenance: They often require less maintenance due to their robust design and resistance to wear, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Versatility: Track rollers are versatile and can be used in various applications, including conveyor systems, cam-driven equipment, and material handling.
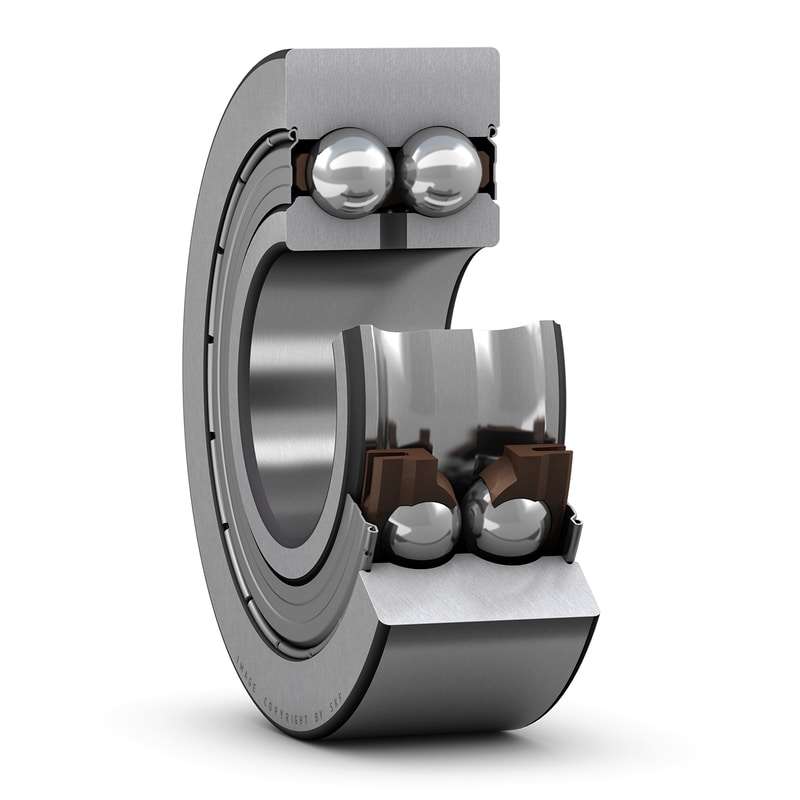
Types of Track Rollers
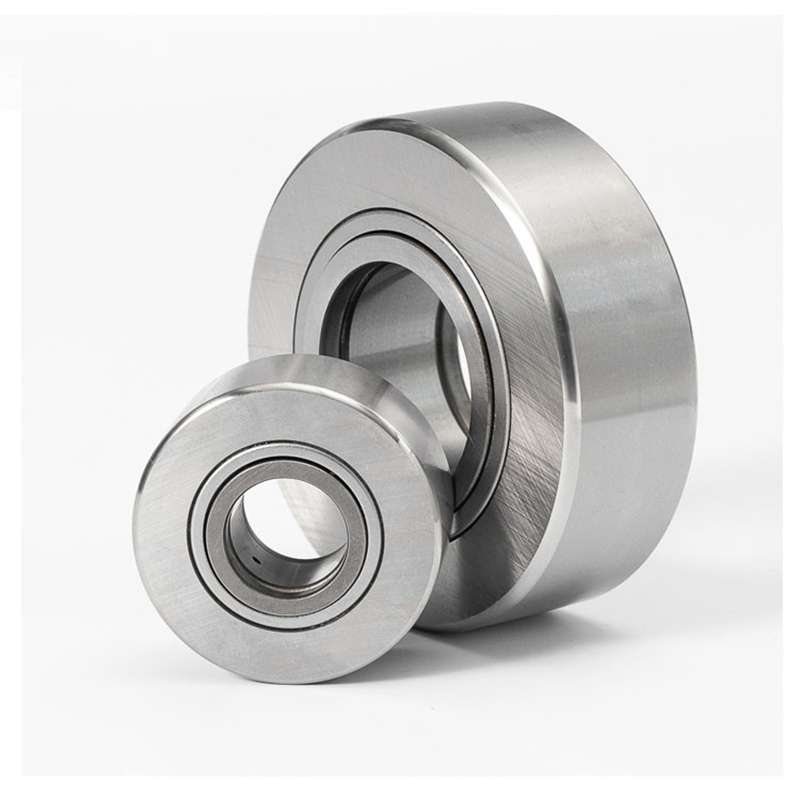
Cam rollers

Cam roller with crowned outside surface, integral sealing and relubrication feature
These cam rollers (yoke-type track rollers) are designed to run on all types of tracks and to be used in cam drives, conveyor systems, etc.

Single row cam roller with crowned outer surface and seals on both sides
Single row cam rollers, with seals on both sides, are designed to run on all types of tracks and to be used in cam drives, conveyor systems, etc.
Support roller

Support roller (yoke-type track roller), without flange rings and inner ring
Support rollers (yoke-type track rollers) are designed to run on all types of tracks and to be used in cam drives, conveyor systems, etc.
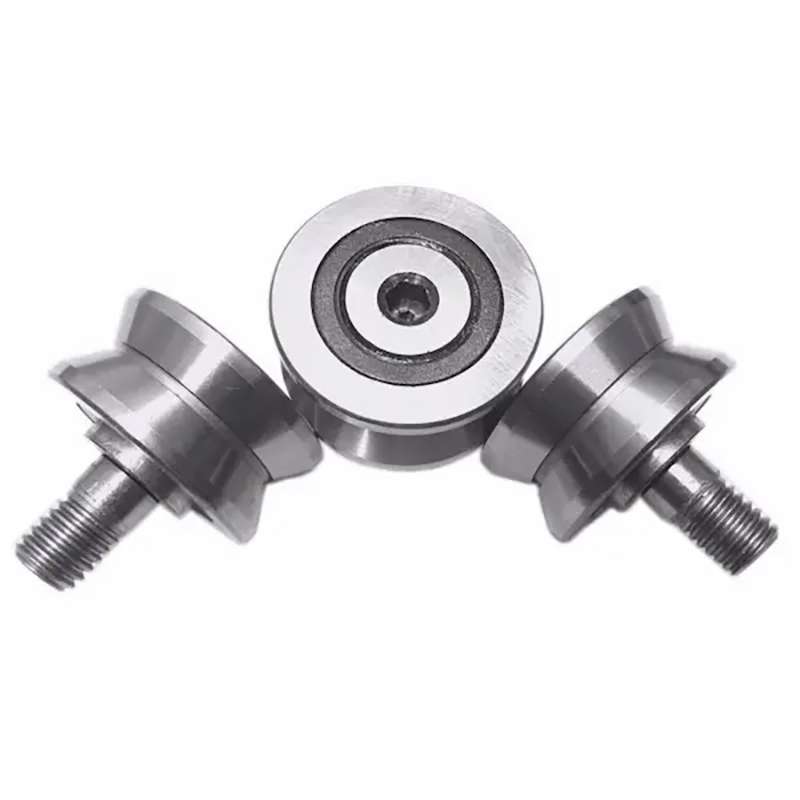
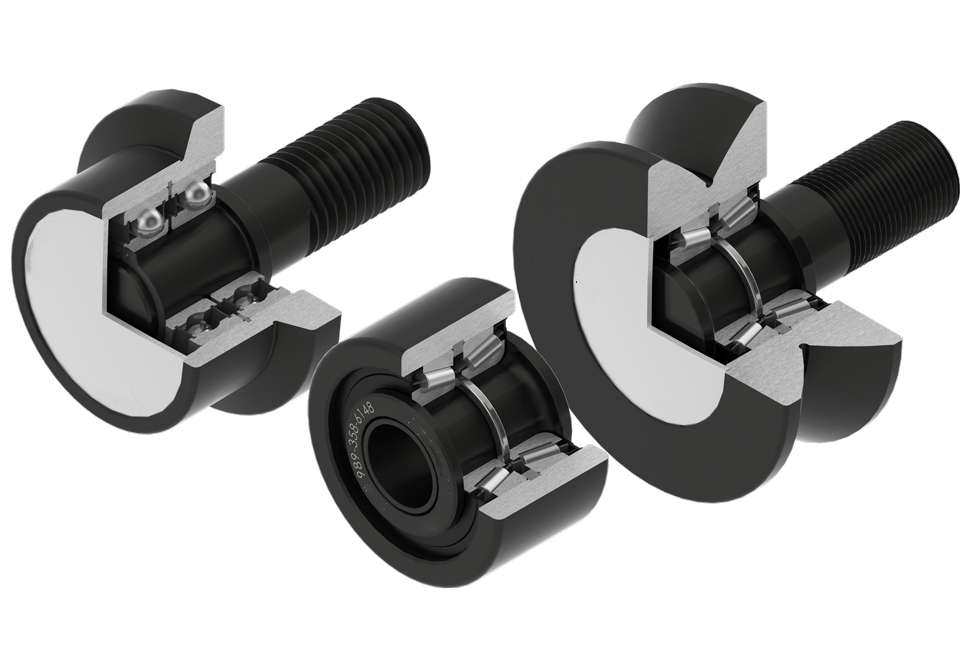
Cam followers

Cam follower (stud-type track roller) with relubrication feature
Cam followers (stud-type track rollers) are designed to run on all types of tracks and to be used in cam drives, conveyor systems, etc.
Applications of Track Rollers

- Material Handling: Track rollers are integral components in conveyor systems, ensuring the smooth movement of materials in warehouses and distribution centers.
- Agriculture: They are used in farm equipment such as combine harvesters and tractors, where they facilitate the movement of components like wheels and treads.
- Cam-Driven Machinery: In machinery with cam profiles, track rollers help convert rotary motion into linear motion, making them essential in manufacturing and automation.
- Construction Equipment: Track rollers are found in construction machinery like excavators and bulldozers, supporting the undercarriage and tracks.
- Material Processing: They are used in crushers and screens in the mining and aggregate industries to ensure efficient material processing.
- Linear Motion Systems: In various linear motion systems, including sliding doors, sliding gates, and adjustable furniture, track rollers enable smooth and controlled movement.
Key Manufacturing Process of Thin section bearings
Material Selection
The process begins with selecting the appropriate material, such as steel, stainless steel, or other specialized materials, based on the application’s requirements.
Turning and Machining
The chosen material is then subjected to turning and machining operations to shape it into the desired dimensions. This step involves processes like CNC machining to create the outer and inner ring components.
Heat Treatment
To enhance the material’s mechanical properties, the components are often subjected to heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering. This step improves hardness, durability, and resistance to wear.
Rolling Element Installation
Rolling elements, such as balls or rollers, are installed within the track roller assembly. This step ensures the bearing can effectively handle radial and axial loads.
Profile Grinding
Track rollers often have specialized profiles, such as V-groove or crowned profiles, to match the specific track or cam configuration. Profile grinding is used to create these shapes accurately.
Surface Finish and Quality Control
The final step involves surface finishing to ensure smooth and precise operation. Comprehensive quality control processes, including inspections and testing, are carried out to guarantee the track rollers meet specified standards and tolerances.


FAQ - Frequently Asked Questions

Signs include increased friction, noise, and reduced smoothness of movement.
Regular maintenance, lubrication, and proper alignment are essential for preventing wear.
Misalignment can occur due to improper installation or excessive load.
Realign the track rollers and ensure the load is distributed evenly.
Exposure to moisture and harsh environments can lead to corrosion.
Use corrosion-resistant materials or coatings and keep them well-lubricated.
Noise can result from wear, lack of lubrication, or misalignment.
Choose a lubricant suitable for the specific application and environment.
Some track rollers are designed for high-temperature applications, while others may not be suitable for extreme heat.
Lack of proper lubrication and excessive load can cause track rollers to seize.
Regularly lubricate the rollers and reduce the load if possible.
Debris and contaminants can accelerate wear and reduce performance.
Use seals and shields, and keep the surrounding environment clean.
Some track rollers are designed for high-speed operation, while others may not be suitable.
Shock loads or inadequate lubrication can lead to flat spots.
Avoid sudden impacts and maintain proper lubrication.
Overloading can lead to premature wear, misalignment, and decreased service life.
Consult with an engineer or refer to manufacturer guidelines for proper sizing.
In some cases, track rollers can be reconditioned, but it’s often more cost-effective to replace them.
The service life varies depending on factors like load, maintenance, and the quality of the track rollers. Proper care can extend their lifespan significantly.
Installation and Maintenance of Track Rollers
Installation
- Preparation: Gather all the necessary tools and equipment, including the track roller assembly, fasteners, and any alignment aids. Ensure that the installation area is clean and free of debris.
- Alignment: Carefully align the track roller with the intended track or cam profile. Ensure that the alignment is precise, as misalignment can lead to premature wear and performance issues.
- Mounting: Securely mount the track roller on the designated stud or shaft. Use the appropriate fasteners, such as bolts or screws, and torque them to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Lubrication: Apply the recommended lubricant to the track roller’s rolling elements and contact surfaces. Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction and preventing premature wear.
- Initial Testing: After installation, conduct initial testing to ensure that the track roller moves smoothly and without any unusual noise or resistance. Make any necessary adjustments if issues are detected.
- Regular Maintenance: Establish a maintenance schedule for the track rollers to ensure they remain in optimal condition. This includes periodic inspections, re-lubrication, and addressing any wear or misalignment issues promptly.
Maintenance:
- Regular Lubrication: Apply the appropriate lubricant to the track roller’s rolling elements and contact surfaces. Lubrication reduces friction and prevents wear.
- Cleaning: Periodically clean the track roller and the surrounding area to remove debris, contaminants, and any buildup of dirt or grime.
- Inspect for Wear: Routinely inspect the track rollers for signs of wear, including flat spots, pitting, or uneven wear on the rolling elements. Replace any worn components.
- Check Alignment: Ensure that the track rollers remain properly aligned with the track or cam profile. Misalignment can lead to premature wear and performance issues.
- Tighten Fasteners: Check and tighten the fasteners used to secure the track rollers to prevent loosening or potential damage due to vibrations or heavy loads.
- Seal Maintenance: If your track rollers have seals or shields, inspect them for damage and replace any that are compromised to maintain protection from contaminants.
- Load Management: Avoid overloading the track rollers beyond their specified capacity. Ensure that the load is evenly distributed to prevent excessive wear.





