Table of Contents
Categories
-
Adapter Sleeves (9)
-
Ball Bearings (11)
-
Ball Screw Bearings (2)
-
Ceramic Bearings (28)
-
Pillow Block Bearings (4)
-
Plain Bearings (32)
-
Roller Bearings (12)
-
Slewing Bearings (43)
-
Sliding Block (3)
-
Stainless Steel Bearings (27)
-
Super Precision Bearings (6)
-
Thin Section Bearings (9)
-
Track Rollers (4)
-
Universal Joints (1)
Bicycle Bearings Basics: What You Need To Know
Introduction
Download FHD Bicycle Bearings Catalogue
Bicycle bearings may seem like small parts, but they play an important role in ensuring a smooth and efficient ride. Bicycle bearings reduce friction between the moving parts of a bicycle, making pedaling easier and steering more precise. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into bicycle bearings, exploring their key components, different types, and the materials used to give you a better understanding of bicycle bearings.
What Are Bicycle Bearings
Bicycle bearings consist of small balls or rollers enclosed between two rings called raceways. The inner ring is fixed to the rotating parts, while the outer ring is fixed to the stationary parts of the bicycle. Allows various parts of the bicycle such as wheels, pedals, and steering to rotate and move smoothly.
Bicycle bearings are important components that allow the various parts of a bicycle to move smoothly with minimal friction. These components are located in key places such as wheels, bottom brackets, pedals, and headsets. Essentially, bearings help reduce wear on the moving parts of a bicycle, making pedaling easier and steering more precise.
The Key Component Bearings
Bottom bracket bearing: Located where the bike crankset meets the frame. Reduces drag for smooth pedaling.
Headset Bearings: Located at the point where your fork connects to the bike frame, play a pivotal role in bike handling.
Wheel Hub Bearings: These are found in the center of your bike’s wheels. Main function is to allow the wheels to spin freely with as little friction as possible.
Frame Bearings: Typically used in performance or mountain bikes with full suspension, are part of the bike’s frame joints. They help maintain the frame’s integrity and flexibility, Absorbs shock and ensures a comfortable ride on rough roads.
Pedal Bearings:are found in the pedals and support their rotation.
Derailleur Bearings: Although Small size. They help the derailleur move smoothly, ensuring quick and accurate shifts between gears.
Types Of Bearings On Bicycles
There are several types of bicycle bearings, each with its own unique characteristics
Loose ball bearings (cup and cone)
The traditional cup and cone design places the loose ball bearing directly between the inner tapered raceway and the outer cup raceway. The tapered raceway is usually threaded onto the axle, while the cup raceway is pressed into the hub housing. This design allows the bearing preload to be adjusted by tightening or loosening the cone.
- Advantages
Bearing preload can be tailored to the desired tightness to optimize performance. Individual bearings can be inspected and replaced for easy maintenance. - Disadvantages:
Regular maintenance and adjustments are required to compensate for bearing wear and settling. Precise adjustments are required to obtain proper preload to avoid binding or excessive clearance.
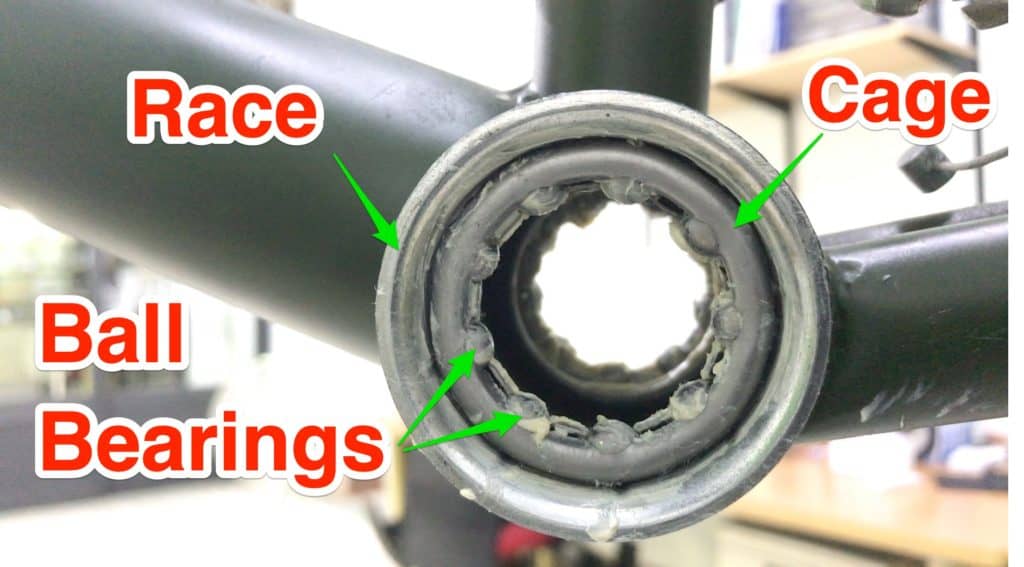
Caged-Ball Bearings
Caged-ball bearings feature balls captured within a cage or retainer, ensuring proper spacing and positioning. This design simplifies installation and maintenance compared to loose ball bearings. The cage holds the bearings in place, preventing them from falling out during handling or assembly.
- Advantages:
Easier to handle and install, reducing the risk of losing or misplacing bearings.
Maintains even ball distribution and prevents ball-to-ball contact, improving performance.
Requires less frequent maintenance than loose ball bearings. - Disadvantages:
The cage itself can wear out over time, reducing bearing life under high stress conditions.
Slightly less customizable preload adjustment compared to loose ball bearings.
Bushing
Bushing , also known as plain bearings, consist of a solid sleeve made of metal, plastic, or other materials that provide a bearing surface. The bushing is typically press-fit into a housing, allowing a shaft or axle to rotate within it. Bushings can be made of different materials to suit various load and friction requirements.
- Advantages:
Simple and inexpensive design, making them cost-effective for many applications.
Durable and able to withstand high radial loads, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Easier to install and maintain compared to ball or roller bearings. - Disadvantages:
Lower precision and smoothness compared to rolling-element bearings.
Susceptible to increased friction and wear without proper lubrication.
Limited axial load capacity compared to other bearing types.
Needle Bearings
Needle bearings, also known as roller bearings, use slender cylindrical rollers instead of balls. The rollers are arranged in a radial pattern, providing a high load-carrying capacity relative to their size. Needle bearings are often used in applications with limited space or high radial loads.
- Advantages:
Compact design suitable for slim, space-constrained applications.
Able to handle high radial loads due to the roller’s line contact.
Good shock and impact resistance compared to ball bearings. - Disadvantages:
Complex installation process, often requiring specialized tools and procedures.
Higher cost compared to some other bearing types.
Limited axial load capacity and susceptibility to misalignment.
Cartridge Bearings
Cartridge bearings, also known as sealed unit bearings, are pre-assembled and sealed units that contain the bearing components (races, balls/rollers, and cage) within a single unit. These bearings are designed to be maintenance-free and easily replaceable as a complete unit.
- Advantages:
Durable and long-lasting due to the sealed design, protecting against contamination.
Waterproof and resistant to dirt, mud, and other environmental contaminants.
Require minimal maintenance, as the bearings are pre-lubricated and sealed.
Easy to replace as a complete unit, simplifying maintenance procedures. - Disadvantages:
Generally more expensive than loose or caged ball bearings.
Limited customization options, as the bearings are pre-assembled units.
Entire unit must be replaced if any component fails, potentially increasing long-term costs.
Materials Used In Bicycle Bearings
In the world of bicycle bearings, there are two main materials: steel and ceramic. Steel bearings are the more traditional choice, offering durability and cost-effectiveness. Steel is strong, durable, able to withstand heavy loads, and is not prone to wear, making it a top choice for everyday riding.
Ceramic bearings, on the other hand, offer distinct advantages. These bearings are lighter than steel bearings and create less friction, which means a smoother ride and potentially faster speeds. However, the trade-off for reduced friction and weight is a higher cost. Ceramic bearings are generally more expensive and may not last as long as steel bearings in harsh conditions.
Bicycle Bearings Sizes Explained
Bicycle bearings vary in size depending on their location and function in the bicycle.
In hubs, bottom brackets, headstocks and pedals, for example, the size of the bearing is usually determined by its inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD) and width in millimeters.
A common bearing size for bicycle hubs might be 6902, which has an ID of 15 mm, an OD of 28 mm, and a width of 7 mm.
Sizing requirements are determined by the specific design and requirements of each bicycle component, with the goal of balancing durability, weight, and performance efficiency.
Signs Of Bicycle Bearing Failure
For brand purchasers, recognizing the signs of bearing failure and addressing them in a timely manner is critical to ensuring the quality and performance of the final product.
- A healthy bearing should run smoothly and quietly. If a bearing test reveals friction, harshness or other unusual noises, this may indicate wear or damage to the bearing.
- If the rotational torque of the bearing is tested and a significant increase in resistance is found compared to normal levels, this may be due to abnormal wear within the bearing. Excessive rotational resistance can seriously affect the transmission efficiency and riding experience of the bicycle.
- Under normal circumstances, high quality bearings should be tightly fitted to the component and the radial clearance should be kept to the minimum level within the specification. If you notice significant wobble or excessive clearance, it may be due to the bearings themselves being out of tolerance or worn.
- When bearings are severely worn or internally contaminated, their rotation will become uneven and discontinuous, and in extreme cases may even be completely stalled.
- In the case of sealed bearings, if there are traces of oil leakage or contaminant infiltration on the periphery of the bearing, this may mean that the seal has failed and the internal contamination has shortened the service life of the bearing considerably.
How To Maintain Your Bearings
As a brand buyer, you should know how to maintain and care for bicycle bearings
First of all, quality control to ensure that the purchased bearing products can withstand the wear and tear of long-term use and environmental impacts, such as water and dust resistance, to meet specific performance requirements and application scenarios. Generally speaking, bearings in critical locations such as base bearings, head tube bearings and wheel bearings need to be inspected regularly.
At the same time, make sure that the specifications of the bearing products match the design of the bicycle, and select high-quality lubricants that are suitable for various usage environments (e.g., wet, dry, dusty, etc.). For non-sealed bearings, proper lubrication must be maintained. It is recommended to use special high quality bearing grease and replenish it regularly according to the usage environment and condition. Excessive or insufficient lubrication can lead to deterioration of bearing performance.
Finally, follow detailed bearing maintenance and care guidelines, including proper cleaning of bearings and lubrication, timely inspection and replacement of worn bearings, development of a maintenance program, and regular follow-up.
Why Are Bearings Important On Bicycle?
Bearings play a vital role in the overall performance and function of a bicycle. These small but critical components are found in several key parts of your bicycle, including the wheels, bottom bracket, pedals, and headset. This is why bearings are so important to your bicycle
1. Runs smoothly
The main role of bearings in bicycle is to promote smooth rotation of the moving parts they support. Bearings minimize friction and drag by allowing components such as wheels and pedals to rotate freely around their axes. This not only makes the bicycle easier to pedal, but also contributes to a more efficient and enjoyable ride.
2. Increase the service life of the bicycle
High-quality bearings have excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance and can maintain good performance in harsh environments and long-term use. In contrast, inferior bearings are easy to wear and will accelerate the wear and tear of other components, thus shortening the service life of the vehicle.
3. Ensure riding safety
The performance of bearings directly affects the stability and reliability of bicycle components. Once the bearings experience abnormal wear or failure, key components such as wheels and handlebars may shake or get stuck, thereby increasing riding risks. High-quality bearings can minimize these potential hazards.
4. Precision and Control
In the headset and bottom bracket, bearings play a key role in the steering and stability of the bike. Smooth, responsive bearings help with precise bike control.
5. Determine riding comfort
No matter what kind of riding environment you are in, smooth bearing rotation can bring a smooth and unimpeded pedaling experience, while inferior bearings will cause bumps and vibrations, affecting the riding quality.
Conclusion: Choosing The Best Bicycle Bearings
High-quality bicycle bearings directly affect the overall performance of the bicycle, including speed, smoothness, and riding comfort.
Mountain bikers who face muddy and rugged trails should give priority to durable steel bearings, while road cyclists who pursue speed may choose lighter ceramic bearings. In terms of cost, higher-priced ceramic bearings may reduce friction and make the ride smoother, but they cost much more than more affordable and extremely durable steel bearings. So when you choose the type of bearing, you should combine it with the application conditions, environment, cost, and the quality of the bearing.
Our bicycle bearings are manufactured using high-end materials and precision craftsmanship, ensuring ultra-high durability and superior performance to meet a variety of riding conditions and needs. In addition, continued use of high-performance bearings reduces maintenance needs and extends the life of the bicycle, further increasing consumer trust in the brand.
We strictly control and become the best supplier in the industry:
- Excellent manufacturing technology and advanced equipment ensure the high precision and dimensional accuracy of the bearings.
- It is made of high-quality wear-resistant steel and undergoes precision heat treatment to ensure that the bearings have outstanding wear resistance and service life.
- Advanced surface treatment and precision machining minimize bearing noise, vibration and starting resistance.
- Special special grease is used to improve the anti-pollution and anti-corrosion properties of the bearings.
We firmly believe that only by selecting the highest quality core components can the performance of the vehicle be maximized.
References
- 1.Some detailed information about “bicycle bearings “from Bikeradar;
- 2. The Ultimate Guide to ”bicycle Bearings “from FIRST Company;
- 3. In-depth analysis and comparison of “bicycle bearing ”types




















